MLKL in cancer: more than a necroptosis regulator
- PMID: 33953348
- PMCID: PMC8184805
- DOI: 10.1038/s41418-021-00785-0
MLKL in cancer: more than a necroptosis regulator
Abstract
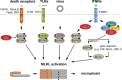
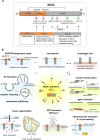
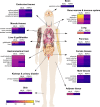
Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL) emerged as executioner of necroptosis, a RIPK3-dependent form of regulated necrosis. Cell death evasion is one of the hallmarks of cancer. Besides apoptosis, some cancers suppress necroptosis-associated mechanisms by for example epigenetic silencing of RIPK3 expression. Conversely, necroptosis-elicited inflammation by cancer cells can fuel tumor growth. Recently, necroptosis-independent functions of MLKL were unraveled in receptor internalization, ligand-receptor degradation, endosomal trafficking, extracellular vesicle formation, autophagy, nuclear functions, axon repair, neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation, and inflammasome regulation. Little is known about the precise role of MLKL in cancer and whether some of these functions are involved in cancer development and metastasis. Here, we discuss current knowledge and controversies on MLKL, its structure, necroptosis-independent functions, expression, mutations, and its potential role as a pro- or anti-cancerous factor. Analysis of MLKL expression patterns reveals that MLKL is upregulated by type I/II interferon, conditions of inflammation, and tissue injury. Overall, MLKL may affect cancer development and metastasis through necroptosis-dependent and -independent functions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Sun L, Wang H, Wang Z, He S, Chen S, Liao D, et al. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein mediates necrosis signaling downstream of RIP3 kinase. Cell. 2012;148:213–27. - PubMed
-
- Pasparakis M, Vandenabeele P. Necroptosis and its role in inflammation. Nature. 2015;517:311–20. - PubMed
-
- Delanghe T, Dondelinger Y, Bertrand MJM. RIPK1 kinase-dependent death: a symphony of phosphorylation events. Trends Cell Biol. 2020;30:189–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Methusalem BOF16/MET_V/007, iBOF20/IBF/039 ATLANTIS/Bijzonder Onderzoeksfonds (Special Research Fund)
- FAF-F/2016/865, F/2020/1505/Stichting Tegen Kanker (Belgian Foundation Against Cancer)
- EOS MODEL-IDI Grant 30826052,esearch grants G.0E04.16N, G.0C76.18N, G.0B71.18N, G.0B96.20N/Belgian National Fund for Scientific Research | Fonds pour la Formation à la Recherche dans l'Industrie et dans l'Agriculture (Training Fund for Research in Industry and Agriculture)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

