Clinical Significance of miR-183-3p and miR-182-5p in NSCLC and Their Correlation
- PMID: 33953608
- PMCID: PMC8089025
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S305179
Clinical Significance of miR-183-3p and miR-182-5p in NSCLC and Their Correlation
Abstract
Purpose: Accumulating evidence has indicated that dysregulated microRNAs (miRNAs) are involved in cancer progression. In this study, we evaluated the clinicopathologic significance of miR-183-3p and miR-182-5p, and the role of miR-183-3p in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression.
Patients and methods: Seventy-six NSCLC patients from Beijing Chest Hospital were included. The expression of miR-183-3p and miR-182-5p was evaluated by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Then, cell growth curve assays and colony formation assays were performed. Bioinformatics analysis of TCGA database was performed to explore the clinicopathological significance and prognostic value.
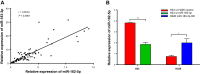
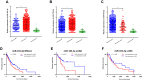
Results: miR-183-3p and miR-182-5p were significantly increased in NSCLC tumor tissues (both P < 0.0001) and were positively correlated (r = 0.8519, P < 0.0001). miR-183-3p (P = 0.0444) and miR-182-5p (P = 0.0132) were correlated with tumor size. In addition, miR-183-3p (P = 0.0135) and miR-182-5p (P = 0.0009) were upregulated in normal lung tissues from smokers. In vitro, miR-183-3p was correlated with cell proliferation. In addition, bioinformatics analysis indicated that miR-183-3p was correlated with poor prognosis (P = 0.0466) and tumor size (P = 0.0017). In addition, miR-183-3p was higher in lung squamous carcinoma (LUSC) tissue (P < 0.0001) than in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) tissue, and miR-183-3p was higher in the tumor tissue of smokers (P = 0.0053) than in that of nonsmokers.
Conclusion: Upregulation of miR-183-3p and miR-182-5p may play an oncogenic role in NSCLC. miR-183-3p could be used as a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target to manage lung cancer.
Keywords: NSCLC; miR-182-5p; miR-183-3p; non-small-cell lung cancer; prognosis; proliferation.
© 2021 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

