Efficacy and Safety of Transarterial Chemoembolization for the Treatment of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Associated with Bile Duct Tumor Thrombus: A Real-World Retrospective Cohort Study
- PMID: 33953609
- PMCID: PMC8089084
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S307065
Efficacy and Safety of Transarterial Chemoembolization for the Treatment of Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma Associated with Bile Duct Tumor Thrombus: A Real-World Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
Background: The occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with bile duct tumor thrombus (BDTT) is rare. The aim of the study was to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for patients with unresectable HCC with BDTT.
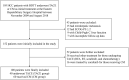
Methods: This retrospective study was conducted on newly diagnosed HCC and BDTT patients who were initially treated with TACE or conservative management (CM) from 2009 to 2018. Survival outcomes of patients treated with TACE were compared with those of patients given CM. Multivariate analyses were performed to identify independent prognostic factors related to survival.
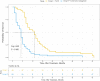
Results: Out of 100 patients included in this study, 40 patients underwent TACE, while the remaining 60 received CM. The median survival time of the TACE group was 8.0 months longer than that of the CM group (13.0 versus 5.0 months, P < 0.001). The 6-, 12-, 18-, 24-month overall survival (OS) rates were 90.0%, 52.5%, 22.5%, and 12.5%, respectively, for the TACE group compared with 26.7%, 8.3%, 5.0%, and 3.3%, respectively, for the CM group. Multivariate analyses showed that treatment allocation (hazard ratio [HR], 0.421; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.243-0.730; P = 0.002), Child-Pugh status (HR, 2.529; 95% CI, 1.300-4.920; P = 0.006) and total bilirubin level (HR, 1.007; 95% CI, 1.004-1.009; P < 0.001) on first admission were independent predictors of OS. There was no procedure-related mortality within one month after TACE treatment.
Conclusion: TACE is a safe and effective treatment method that may improve the OS of patients with unresectable HCC with BDTT.
Keywords: bile duct tumor thrombus; conservative management; hepatocellular carcinoma; overall survival; transarterial chemoembolization.
© 2021 Feng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Jin-Kai Feng, Ju-Xian Sun, Zong-Han Liu, and Jing-Wen Gu are co-first authors for this study. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest related to this study.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

