MINSTED fluorescence localization and nanoscopy
- PMID: 33953795
- PMCID: PMC7610723
- DOI: 10.1038/s41566-021-00774-2
MINSTED fluorescence localization and nanoscopy
Abstract
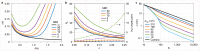
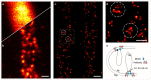
We introduce MINSTED, a fluorophore localization and super-resolution microscopy concept based on stimulated emission depletion (STED) that provides spatial precision and resolution down to the molecular scale. In MINSTED, the intensity minimum of the STED doughnut, and hence the point of minimal STED, serves as a movable reference coordinate for fluorophore localization. As the STED rate, the background and the required number of fluorescence detections are low compared with most other STED microscopy and localization methods, MINSTED entails substantially less fluorophore bleaching. In our implementation, 200-1,000 detections per fluorophore provide a localization precision of 1-3nm in standard deviation, which in conjunction with independent single fluorophore switching translates to a -100-fold improvement in far-field microscopy resolution over the diffraction limit. The performance of MINSTED nanoscopy is demonstrated by imaging the distribution of Mic60 proteins in the mitochondrial inner membrane of human cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests S.W.H. benefits from intellectual property on the described localization and nanoscopy owned by the Max Planck Society.
Figures


References
-
- Hell SW, Wichmann J. Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated emission: stimulated-emission-depletion fluorescence microscopy. Opt Lett. 1994;19:780–782. - PubMed
-
- Westphal V, Hell SW. Nanoscale resolution in the focal plane of an optical microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 2005;94:143903. - PubMed
-
- Hell SW. Far-field optical nanoscopy. Science. 2007;316:1153–1158. - PubMed
-
- Danzl JG, et al. Coordinate-targeted fluorescence nanoscopy with multiple off states. Nat Photonics. 2016;10:122–128.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
