The Effect of Two Types of Exercise Preconditioning on the Expression of TrkB, TNF- α, and MMP2 Genes in Rats with Stroke
- PMID: 33954182
- PMCID: PMC8057886
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5595368
The Effect of Two Types of Exercise Preconditioning on the Expression of TrkB, TNF- α, and MMP2 Genes in Rats with Stroke
Abstract
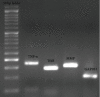
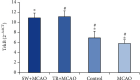
Despite the beneficial effects of exercise and physical activity, there is little knowledge about the effects of different types of physical activity on neural function. The present study assessed the effects of two types of selected aerobic exercises prior to stroke induction and characterized the expression of TrkB, TNF-α, and MMP2 genes in vivo. Forty male adult Wistar rats were exposed to aerobic exercises following randomization into four groups, including swimming + MCAO (Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion) (n = 10), treadmill training + MCAO (n = 10), MCAO (n = 10), and control (n = 10). The swimming + MCAO group included swimming for 30 minutes each day, while the treadmill training + MCAO group program involved running for 30 minutes each day at an intensity of 15 m/min, for three weeks, five days a week. Neurological deficit was assessed using modified criteria at 24 h after the onset of cerebral ischemia. In the control group, the animals worked freely for three weeks without undergoing ischemia. The MCAO group also operated freely for three weeks after they underwent a stroke. Both training groups underwent ischemia after three weeks of training. TrkB, TNF-α, and MMP2 gene expressions were increased in the MCAO+ swimming training and in the MCAO + running training group compared to the control and MCAO groups, respectively. Preconditioning aerobic exercises significantly increased brain trophic support and reduced brain damage conditions in exercise groups, which support the importance of aerobic exercise in the prevention and treatment of stroke.
Copyright © 2021 Mostafa Teymuri Kheravi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

