The BNT162b2 vaccine is associated with lower new COVID-19 cases in nursing home residents and staff
- PMID: 33955567
- PMCID: PMC8242377
- DOI: 10.1111/jgs.17224
The BNT162b2 vaccine is associated with lower new COVID-19 cases in nursing home residents and staff
Abstract
Background/objectives: The effectiveness of the BNT162b2 vaccine on preventing the spread of COVID-19 and deaths in nursing homes (NH) is unknown.
Design: We used zero-inflated negative binomial mixed effects regressions to model the associations of time since the vaccine clinic ending the week of December 27, 2020 (cohort 1), January 3, 2021 (cohort 2), or January 10, 2021 (cohort 3) controlling for county rate of COVID-19, bed size, urban location, racial and ethnic census, and level of registered nurses with resident cases and deaths of COVID-19 and staff cases of COVID-19.
Setting and participants: All 2501 NHs who held a vaccine clinic from the first 17 states to initiate clinics as part of the Pharmacy Partnership for Long-Term Care Program.
Main outcome(s) and measure(s): Adjusted Incidence Rate Ratio (IRR) for time in 3, 4, 5, and 6 weeks after the first vaccine clinic for resident cases and deaths of COVID-19 and staff cases of COVID-19.
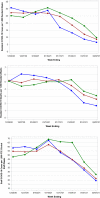
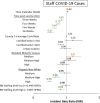
Results: Resident and staff cases trended downward in all three cohorts following the vaccine clinics. Time following the first clinic at 5 and 6 weeks was consistently associated with fewer resident cases (IRR: 0.68 [95% CI: 0.54-0.84], IRR: 0.64 [95% CI: 0.48-0.86], respectively); resident deaths (IRR: 0.59 [95% CI: 0.45-0.77], IRR: 0.45 [95% CI: 0.31-0.65], respectively); and staff cases (IRR: 0.64 [95% CI: 0.56-0.73], IRR: 0.51 [95% CI: 0.42-0.62], respectively). Other factors associated with fewer resident and staff cases included facilities with less than 50 certified beds and high nurse staffing per resident day (>0.987). Contrary to prior research, higher Hispanic non-white resident census was associated with fewer resident cases (IRR: 0.42, 95% CI: 0.31-0.56) and deaths (IRR: 0.18, 95% CI: 0.12-0.27).
Conclusions: The BNT162b2 vaccine is associated with decreased spread of SARS-CoV-2 in both residents and staff as well as decreased deaths among residents.
Keywords: BNT162b2; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; health care worker; mortality; nursing home; vaccination.
© 2021 The American Geriatrics Society.
Conflict of interest statement
David Gifford reports no financial conflicts of interest. He reports the following potential personal conflicts of interests: his spouse serves in state government as acting Commissioner of Public Health and Commissioner of Social Services in the state of Connecticut where she is responsible for the COVID‐19 vaccine program, nursing home licensure, and Medicaid. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- NYT . More than one‐third of U.S. coronavirus deaths are linked to nursing homes. New York Times. February 2, 2021. https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2020/us/coronavirus-nursing-homes.html.
-
- Comas‐Herrera A, Zalakaín J, Lemmon E, et al. Mortality associated with COVID‐19 outbreaks in care homes: early international evidence. International Long‐Term Care Policy Network. 2020. October 14, 2020. https://ltccovid.org/2020/04/12/mortality-associated-with-covid-19-outbr....
-
- Chidambaram P, Garfield R, Neuman T. COVID‐19 has claimed the lives of 100,000 Long‐term care residents and staff. Kaiser Family Foundation. November 25, 2020. https://www.kff.org/policy‐watch/covid‐19‐has‐claimed‐the‐lives‐of‐10000....
-
- Chidambaram P, Garfield R. Patterns in COVID‐19 cases and deaths in long‐term care facilities in 2020. Kaiser Family Foundation. January 14, 2021. https://www.kff.org/coronavirus‐covid‐19/issue‐brief/patterns‐in‐covid‐1....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

