Exosomes derived from MSC pre-treated with oridonin alleviates myocardial IR injury by suppressing apoptosis via regulating autophagy activation
- PMID: 33955654
- PMCID: PMC8184716
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16558
Exosomes derived from MSC pre-treated with oridonin alleviates myocardial IR injury by suppressing apoptosis via regulating autophagy activation
Abstract
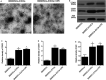
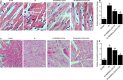
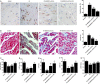
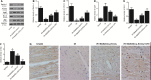
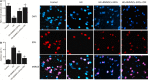
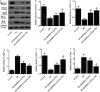
This study aimed to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying the role of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMMSCs)-derived exosomes in ischaemia/reperfusion (IR)-induced damage, and the role of oridonin in the treatment of IR. Exosomes were isolated from BMMSCs. Western blot analysis was done to examine the expression of proteins including CD63, CD8, apoptotic-linked gene product 2 interacting protein X (AliX), Beclin-1, ATG13, B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2), apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1 (Apaf1) and Bcl2-associated X (Bax) in different treatment groups. Accordingly, the expression of CD63, CD81 and AliX was higher in BMMSCs-EXOs and IR + BMMSCs-EXOs + ORI groups compared with that in the BMMSCs group. And BMMSCs-derived exosomes inhibited the progression of IR-induced myocardial damage, while this protective effect was boosted by the pre-treatment with oridonin. Moreover, Beclin-1, ATG13 and Bcl-2 were significantly down-regulated while Apaf1 and Bax were significantly up-regulated in IR rats. And the presence of BMMSCs-derived exosomes partly alleviated IR-induced dysregulation of these proteins, while the oridonin pre-treatment boosted the effect of these BMMSCs-derived exosomes. The inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis of H9c2 cells induced by hypoxia/reperfusion (HR) were mitigated by the administration of BMMSCs-derived exosomes. Meanwhile, HR also induced down-regulation of Beclin-1, ATG13 and Bcl-2 expression and up-regulation of Apaf1 and Bax, which were mitigated by the administration of BMMSCs-derived exosomes. And oridonin pre-treatment boosted the effect of BMMSCs-derived exosomes. In conclusion, our results validated that BMMSCs-derived exosomes suppressed the IR-induced damages by participating in the autophagy process, while the pre-treatment with oridonin could boost the protective effect of BMMSCs-derived exosomes.
Keywords: apoptosis; autophagy; exosomes; mesenchymal stem cells.; myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion; oridonin.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosomal miR-455-3p from BMMSCs prevents cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022 Jan-Dec;41:9603271221102508. doi: 10.1177/09603271221102508. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35577544
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate D-GaIN/LPS-induced hepatocyte apoptosis by activating autophagy in vitro.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Aug 19;13:2887-2897. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S220190. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31695322 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Rescue Myocardial Ischaemia/Reperfusion Injury by Inducing Cardiomyocyte Autophagy Via AMPK and Akt Pathways.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(1):52-68. doi: 10.1159/000480317. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28848091
-
The functional mechanism of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of animal models with Alzheimer's disease: crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Mar 3;13(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02765-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35241159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Cardioprotection: A Novel Application to Prevent Myocardial Injury.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Sep 13;23(9):310. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2309310. eCollection 2022 Sep. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 39077717 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Effects of Colchicum Dispert and Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy on Skeletal Muscle Injury in a Rat Aortic Ischemia-Reperfusion Model.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Aug 16;11(8):251. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11080251. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 39195159 Free PMC article.
-
BCL-2 overexpression exosomes promote the proliferation and migration of mesenchymal stem cells in hypoxic environment for skin injury in rats.J Biol Eng. 2025 Jan 17;19(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13036-024-00471-y. J Biol Eng. 2025. PMID: 39825412 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes: a new era in cardiac regeneration.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 Jan 23;16(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-04123-2. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 39849585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Powerful Tool in the Treatment of Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Natural and Nanoscale Modified Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 Dec 28;18:8099-8112. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S443716. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 38164265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles for delivering therapeutic agents in ischemia/reperfusion injury.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2024 Dec;19(6):100965. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2024.100965. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2024. PMID: 39640057 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yellon DM, Hausenloy DJ. Myocardial reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med. 2007;357:1121‐1135. - PubMed
-
- Ferdinandy P, Schulz R, Baxter GF. Interaction of cardiovascular risk factors with myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury, preconditioning, and postconditioning. Pharmacol Rev. 2007;59:418‐458. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

