Responsive neurostimulation for focal motor status epilepticus
- PMID: 33955717
- PMCID: PMC8164849
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.51318
Responsive neurostimulation for focal motor status epilepticus
Abstract
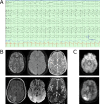
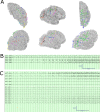
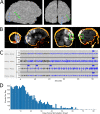
No clear evidence-based treatment paradigm currently exists for refractory and super-refractory status epilepticus, which can result in significant mortality and morbidity. While patients are typically treated with antiepileptic drugs and anesthetics, neurosurgical neuromodulation techniques can also be considered. We present a novel case in which responsive neurostimulation was used to effectively treat a patient who had developed super-refractory status epilepticus, later consistent with epilepsia partialis continua, that was refractory to antiepileptic drugs, immunomodulatory therapies, and transcranial magnetic stimulation. This case demonstrates how regional therapy provided by responsive neurostimulation can be effective in treating super-refractory status epilepticus through neuromodulation of seizure networks.
© 2021 The Authors. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The MGH Translational Research Center has a clinical research support agreement with Neuralink, Paradromics, and Synchron, for which LRH and SSC provide consultative input.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Emergent responsive neurostimulation in pediatric super-refractory epilepsia partialis continua.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024 Dec;11(12):3320-3327. doi: 10.1002/acn3.52199. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39540465 Free PMC article.
-
Neurostimulation in the treatment of refractory and super-refractory status epilepticus.Epilepsy Behav. 2019 Dec;101(Pt B):106551. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.106551. Epub 2019 Oct 30. Epilepsy Behav. 2019. PMID: 31676239 Review.
-
Novel Use of Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS System) in the Treatment of Super Refractory Status Epilepticus.J Clin Neurophysiol. 2019 May;36(3):242-245. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0000000000000541. J Clin Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 30531428
-
Responsive neurostimulation as a treatment for super-refractory focal status epilepticus: a systematic review and case series.J Neurosurg. 2023 Jun 9;140(1):201-209. doi: 10.3171/2023.4.JNS23367. Print 2024 Jan 1. J Neurosurg. 2023. PMID: 37329518
-
Epilepsia partialis continua responsive to neocortical electrical stimulation.Epilepsia. 2015 Aug;56(8):e104-9. doi: 10.1111/epi.13067. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Epilepsia. 2015. PMID: 26174165
Cited by
-
Neuromodulation Techniques in Children with Super-Refractory Status Epilepticus.Brain Sci. 2023 Oct 30;13(11):1527. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13111527. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 38002487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surgical management of status epilepticus: A systematic review.Epilepsia Open. 2024 Jun;9(3):850-864. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12924. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Epilepsia Open. 2024. PMID: 38456595 Free PMC article.
-
Emergent responsive neurostimulation in pediatric super-refractory epilepsia partialis continua.Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024 Dec;11(12):3320-3327. doi: 10.1002/acn3.52199. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Ann Clin Transl Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39540465 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term Effect of Multichannel tDCS Protocol in Patients with Central Cortex Epilepsies Associated with Epilepsia Partialis Continua.Brain Topogr. 2024 Sep;37(5):897-906. doi: 10.1007/s10548-024-01045-3. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Brain Topogr. 2024. PMID: 38446345
References
-
- Trinka E, Kälviäinen R. 25 years of advances in the definition, classification and treatment of status epilepticus. Seizure 2017;44:65–73. - PubMed
-
- Shorvon S. Super‐refractory status epilepticus: An approach to therapy in this difficult clinical situation. Epilepsia 2011;52(s8):53–56. - PubMed
-
- Costello DJ, Kilbride RD, Cole AJ. Cryptogenic New Onset Refractory Status Epilepticus (NORSE) in adults—infectious or not? J Neurol Sci 2009;277:26–31. - PubMed
-
- Trinka E, Cock H, Hesdorffer D, et al. A definition and classification of status epilepticus – report of the ILAE Task Force on Classification of Status Epilepticus. Epilepsia 2015;56:1515–1523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
