Blood Clotting and the Pathogenesis of Types I and II Hereditary Angioedema
- PMID: 33956309
- PMCID: PMC8272707
- DOI: 10.1007/s12016-021-08837-6
Blood Clotting and the Pathogenesis of Types I and II Hereditary Angioedema
Abstract
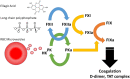
The plasma contact system is the initiator of the intrinsic pathway of coagulation and the main producer of the inflammatory peptide bradykinin. When plasma is exposed to a negatively charged surface the two enzymes factor XII (FXII) and plasma prekallikrein (PK) bind to the surface alongside the co-factor high molecular weight kininogen (HK), where PK is non-covalently bound to. Here, FXII and PK undergo a reciprocal activation feedback loop that leads to full contact system activity in a matter of seconds. Although naturally occurring negatively charged surfaces have shown to be involved in the role of the contact system in thrombosis, such surfaces are elusive in the pathogenesis of bradykinin-driven hereditary angioedema (HAE). In this review, we will explore the molecular mechanisms behind contact system activation, their assembly on the endothelial surface, and their role in the HAE pathophysiology.
Keywords: Angioedema; Bradykinin; Coagulation; Contact activation.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CM has been a speaker for Shire/Takeda. SdM declares no conflict of interest. APK is a consultant/lecturer for CSL Behring, BioCryst, and Pharming.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

