Pathophysiological roles of myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS) in hematological malignancies
- PMID: 33958003
- PMCID: PMC8101130
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-021-00286-9
Pathophysiological roles of myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS) in hematological malignancies
Abstract
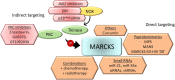
The myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS) protein has been at the crossroads of multiple signaling pathways that govern several critical operations in normal and malignant cellular physiology. Functioning as a target of protein kinase C, MARCKS shuttles between the phosphorylated cytosolic form and the unphosphorylated plasma membrane-bound states whilst regulating several molecular partners including, but not limited to calmodulin, actin, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate, and phosphoinositide-3-kinase. As a result of these interactions, MARCKS directly or indirectly modulates a host of cellular functions, primarily including cytoskeletal reorganization, membrane trafficking, cell secretion, inflammatory response, cell migration, and mitosis. Recent evidence indicates that dysregulated expression of MARCKS is associated with the development and progression of hematological cancers. While it is understood that MARCKS impacts the overall carcinogenesis as well as plays a part in determining the disease outcome in blood cancers, we are still at an early stage of interpreting the pathophysiological roles of MARCKS in neoplastic disease. The situation is further complicated by contradictory reports regarding the role of phosphorylated versus an unphosphorylated form of MARCKS as an oncogene versus tumor suppressor in blood cancers. In this review, we will investigate the current body of knowledge and evolving concepts of the physical properties, molecular network, functional attributes, and the likely pathogenic roles of MARCKS in hematological malignancies. Key emphasis will also be laid upon understanding the novel mechanisms by which MARCKS determines the overall disease prognosis by playing a vital role in the induction of therapeutic resistance. Additionally, we will highlight the importance of MARCKS as a valuable therapeutic target in blood cancers and will discuss the potential of existing strategies available to tackle MARCKS-driven blood cancers.
Keywords: Drug resistance; Hematological cancers; MARCKS; Targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS): a multirole signaling protein in cancers.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017 Dec;36(4):737-747. doi: 10.1007/s10555-017-9709-6. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017. PMID: 29039083 Review.
-
The myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrates (MARCKS): A membrane-anchored mediator of the cell function.Autoimmun Rev. 2021 Nov;20(11):102942. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102942. Epub 2021 Sep 10. Autoimmun Rev. 2021. PMID: 34509657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the effector domain of the myristoylated alanine rich C-kinase substrate enhances lung cancer radiation sensitivity.Int J Oncol. 2015 Mar;46(3):1079-88. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2799. Epub 2014 Dec 17. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25524703
-
Membrane association of the myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate (MARCKS) protein. Mutational analysis provides evidence for complex interactions.J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 2;270(22):13436-45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.22.13436. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7768946
-
Fibroblast Migration Is Regulated by Myristoylated Alanine-Rich C-Kinase Substrate (MARCKS) Protein.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 19;8(6):e66512. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066512. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840497 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Role of MARCKS in Metastasis and Treatment Resistance of Solid Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 8;14(19):4925. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194925. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Profile of MicroRNA Expression and Potential Role in the Regulation of Drug-Resistant Genes in Doxorubicin and Topotecan Resistant Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 23;23(10):5846. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105846. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628654 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Kinase C (PKC) in Neurological Health: Implications for Alzheimer's Disease and Chronic Alcohol Consumption.Brain Sci. 2024 May 29;14(6):554. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14060554. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased MARCKS Activity in BRAF Inhibitor-Resistant Melanoma Cells Is Essential for Their Enhanced Metastatic Behavior Independent of Elevated WNT5A and IL-6 Signaling.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 10;14(24):6077. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246077. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551563 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative gene regulatory networks modulating APOE expression in microglia and astrocytes.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 22:2024.04.19.24306098. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.19.24306098. medRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38699303 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

