Paving the way towards an effective treatment for multiple sclerosis: advances in cell therapy
- PMID: 33958746
- PMCID: PMC8167140
- DOI: 10.1038/s41423-020-00618-z
Paving the way towards an effective treatment for multiple sclerosis: advances in cell therapy
Abstract
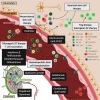
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a leading cause of chronic neurological disability in young to middle-aged adults, affecting ~2.5 million people worldwide. Currently, most therapeutics for MS are systemic immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory drugs, but these drugs are unable to halt or reverse the disease and have the potential to cause serious adverse events. Hence, there is an urgent need for the development of next-generation treatments that, alone or in combination, stop the undesired autoimmune response and contribute to the restoration of homeostasis. This review analyzes current MS treatments as well as different cell-based therapies that have been proposed to restore homeostasis in MS patients (tolerogenic dendritic cells, regulatory T cells, mesenchymal stem cells, and vaccination with T cells). Data collected from preclinical studies performed in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of MS in animals, in vitro cultures of cells from MS patients and the initial results of phase I/II clinical trials are analyzed to better understand which parameters are relevant for obtaining an efficient cell-based therapy for MS.
Keywords: autoimmunity; cell-based therapy; multiple sclerosis; neuroprotection; tolerance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Lublin FD, Reingold SC. Defining the clinical course of multiple sclerosis: results of an international survey. Neurology. 1996;46:907–911. - PubMed
-
- Thompson AJ, et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17:162–173. - PubMed
-
- Bielekova B, Sung M-H, Kadom N, Simon R, McFarland H, Martin R. Expansion and functional relevance of high-avidity myelin-specific CD4 + T cells in multiple sclerosis. J. Immunol. 2004;172:3893–3904. - PubMed
-
- Olsson T, Barcellos LF, Alfredsson L. Interactions between genetic, lifestyle and environmental risk factors for multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2016;13:26–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

