Integrating Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation to Decipher the Mechanism of Action of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction in Treating Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 33958856
- PMCID: PMC8096424
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S304911
Integrating Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation to Decipher the Mechanism of Action of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction in Treating Atherosclerosis
Abstract
Background: This study used network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental validation to assess the effects of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction (HLJDD) on atherosclerosis (AS).
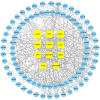
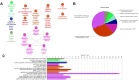
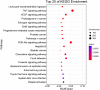
Methods: The components and targets of HLJDD were analyzed using the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology database, and information on the genes associated with AS was retrieved from the GeneCards and OMIM platforms. Protein-protein interactions were analyzed using the STRING platform. A component-target-disease network was constructed using Cytoscape. GO and KEGG analyses were performed to identify molecular biological processes and signaling pathways, and the predictions were verified experimentally. Molecular docking was conducted with ChemOffice software, PyMOL software and Vina to verify the correlation of targets and compounds.
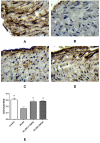
Results: HLJDD contained 31 active compounds, with quercetin, kaempferol, moupinamide and 5-hydroxy-7-methoxy-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)chromone as the core compounds. The most important biotargets of HLJDD in AS were ICAM-1, CD31 and RAM-11. The molecular docking results showed that the molecular docking interaction energy between the 3 key targets and the 4 high-degree components were much less than -5 kJ∙mol-1. The experimental validation results showed that HLJDD might treat AS mainly by reducing TC, TG and LDL-C and increasing HDL-C, upregulating CD31 expression, reducing ICAM-1 and RAM-11 expression, and downregulating inflammatory factors, including CRP, IL-6 and TNF-α. These results support the network pharmacology data and demonstrate that HLJDD affects the expression of core genes and alters the leukocyte transendothelial migration signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Based on network pharmacology and experimental validation, our study indicated that HLJDD exerted anti-AS effect through upregulating CD31 expression and reducing the expression of ICAM-1 and RAM-11. HLJDD may be a potential therapeutic drug to the prevention of AS.
Keywords: Huanglian Jiedu Decoction; atherosclerosis; experimental validation; molecular docking; network pharmacology.
© 2021 Liang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanisms of Huanglian Jiedu decoction in treating Alzheimer's disease by regulating microbiome via network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Mar 16;13:1140945. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1140945. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37009506 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanism of the Effect of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.J Diabetes Res. 2020 Oct 19;2020:5273914. doi: 10.1155/2020/5273914. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 33134394 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology prediction and molecular docking-based strategy to explore the potential mechanism of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction against sepsis.Comput Biol Med. 2022 May;144:105389. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105389. Epub 2022 Mar 9. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35303581 Review.
-
Systems pharmacology, proteomics and in vivo studies identification of mechanisms of cerebral ischemia injury amelioration by Huanglian Jiedu Decoction.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;293:115244. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115244. Epub 2022 Apr 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35378193
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
Cited by
-
Huanglian Jiedu decoction alleviates neurobehavioral damage in mice with chronic alcohol exposure through the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 12;10(8):e29556. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29556. eCollection 2024 Apr 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38644875 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms Underlying the Action of Ziziphi Spinosae Semen in the Treatment of Insomnia: A Study Involving Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 24;12:752211. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.752211. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 35002696 Free PMC article.
-
Effects and mechanisms of Zhizi Chuanxiong herb pair against atherosclerosis: an integration of network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation.Chin Med. 2024 Jan 11;19(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00874-x. Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 38212797 Free PMC article.
-
The Mechanism of Plantaginis Semen in the Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(3):363-379. doi: 10.2174/1871530323666230915100355. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37718520
-
Recent advances of traditional Chinese medicine against cardiovascular disease: overview and potential mechanisms.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Sep 30;15:1366285. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1366285. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39403576 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, et al.; American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139(10):e56–e528. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arnett DK, Blumenthal RS, Albert MA, et al. 2019 ACC/AHA guideline on the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2019;140(11):e596–e646. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000678 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

