Digital PCR Detection of mtDNA/gDNA Ratio in Embryo Culture Medium for Prediction of Embryo Development Potential
- PMID: 33958889
- PMCID: PMC8096441
- DOI: 10.2147/PGPM.S304747
Digital PCR Detection of mtDNA/gDNA Ratio in Embryo Culture Medium for Prediction of Embryo Development Potential
Abstract
Purpose: The ratio of mitochondrial DNA to genomic DNA (mtDNA/gDNA) in embryo culture medium as a predictor of embryonic development is a new method of noninvasive embryo screening. However, current tests based on this concept have proven inconsistent. The aim of this study was to define the predictive value of the ratio of mtDNA/gDNA for embryonic developmental potential.
Materials and methods: We used digital PCR to measure mtDNA/gDNA ratios in day 3 culture media of 223 embryos from 56 patients. We compared the relationship between the predictive value of mtDNA/gDNA ratio and each of embryo fragmentation, embryo morphological grade, and blastocyst formation.
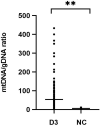
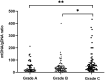
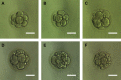
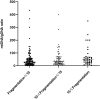
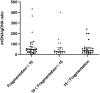
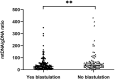
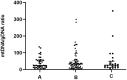
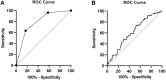
Results: mtDNA/gDNA ratio decreased significantly with a decrease in embryo rating: 22.54 (44.66); 31.25 (36.97) and 46.33 (57.11); Grades A vs C, P = 0.006; B vs C, P = 0.015. mtDNA/gDNA ratio increased overall with an increase in embryo fragment content but did not differ significantly between high-, -medium, and poor-quality embryos. Interestingly, this trend differed from that of the unformed blastocysts. mtDNA/gDNA ratio of cleavage stage embryos forming blastocysts was lower (P=0.005). Trends of mtDNA/gDNA ratio differed according to inner cell mass (ICM) and trophectoderm (TE) levels, but not significantly. mtDNA/gDNA ratio in day 3 culture medium was not significantly improved over morphological scores.
Conclusion: We hereby show the correlation of mtDNA/gDNA ratio in the culture medium of developing embryos. The correlation between the mtDNA/gDNA ratio and early embryonic development was controversial. Furthermore, an increase in mtDNA/gDNA ratio might indicate reduced development potential, but the difference remains insufficient for application as a clinical predictor.
Keywords: blastocyst; digital PCR; embryo; mtDNA/gDNA.
© 2021 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mitochondrial DNA in Day 3 embryo culture medium is a novel, non-invasive biomarker of blastocyst potential and implantation outcome.Mol Hum Reprod. 2014 Dec;20(12):1238-46. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gau086. Epub 2014 Sep 17. Mol Hum Reprod. 2014. PMID: 25232043
-
Non-invasive mitochondrial DNA quantification on Day 3 predicts blastocyst development: a prospective, blinded, multi-centric study.Mol Hum Reprod. 2019 Sep 1;25(9):527-537. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaz032. Mol Hum Reprod. 2019. PMID: 31174207
-
Mitochondrial DNA content in embryo culture medium is significantly associated with human embryo fragmentation.Hum Reprod. 2013 Oct;28(10):2652-60. doi: 10.1093/humrep/det314. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Hum Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23887072 Clinical Trial.
-
Mitochondrial DNA and genomic DNA ratio in embryo culture medium is not a reliable predictor for in vitro fertilization outcome.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 29;9(1):5378. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41801-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30926852 Free PMC article.
-
The Ratio of Mitochondrial DNA to Genomic DNA Copy Number in Cumulus Cell May Serve as a Biomarker of Embryo Quality in IVF Cycles.Reprod Sci. 2021 Sep;28(9):2495-2502. doi: 10.1007/s43032-021-00532-3. Epub 2021 Mar 10. Reprod Sci. 2021. PMID: 33689162
Cited by
-
Day 2 versus day 3 embryo transfer in patients with in vitro fertilization and only one zygote with two pronuclei.J Int Med Res. 2024 Mar;52(3):3000605241233985. doi: 10.1177/03000605241233985. J Int Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38548469 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive evaluation of embryo quality for the selection of transferable embryos in human in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer.Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2022 Dec;49(4):225-238. doi: 10.5653/cerm.2022.05575. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2022. PMID: 36482497 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number in Cleavage Stage Human Embryos-Impact on Infertility Outcome.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Jan 9;44(1):273-287. doi: 10.3390/cimb44010020. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35723399 Free PMC article.
-
The role of mitochondrial DNA copy number in spent culture medium in predicting outcomes of single blastocyst transfer.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2025 Jul;42(7):2207-2218. doi: 10.1007/s10815-025-03507-4. Epub 2025 May 22. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2025. PMID: 40405034
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

