Application of the Mirror Technique for Three-Dimensional Electron Microscopy of Neurochemically Identified GABA-ergic Dendrites
- PMID: 33958990
- PMCID: PMC8093522
- DOI: 10.3389/fnana.2021.652422
Application of the Mirror Technique for Three-Dimensional Electron Microscopy of Neurochemically Identified GABA-ergic Dendrites
Abstract
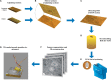
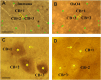
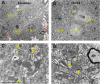
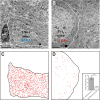
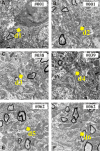
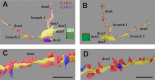
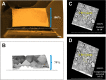
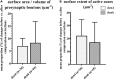
In the nervous system synaptic input arrives chiefly on dendrites and their type and distribution have been assumed pivotal in signal integration. We have developed an immunohistochemistry (IH)-correlated electron microscopy (EM) method - the "mirror" technique - by which synaptic input to entire dendrites of neurochemically identified interneurons (INs) can be mapped due preserving high-fidelity tissue ultrastructure. Hence, this approach allows quantitative assessment of morphometric parameters of synaptic inputs along the whole length of dendrites originating from the parent soma. The method exploits the fact that adjoining sections have truncated or cut cell bodies which appear on the common surfaces in a mirror fashion. In one of the sections the histochemical marker of the GABAergic subtype, calbindin was revealed in cell bodies whereas in the other section the remaining part of the very same cell bodies were subjected to serial section EM to trace and reconstruct the synaptology of entire dendrites. Here, we provide exemplary data on the synaptic coverage of two dendrites belonging to the same calbindin-D28 K immunopositive IN and determine the spatial distribution of asymmetric and symmetric synapses, surface area and volume of the presynaptic boutons, morphometric parameters of synaptic vesicles, and area extent of the active zones.
Keywords: 3D-TEM; GABA interneurons; calbindin; dendritic synaptome; electron microscopy; mirror technique.
Copyright © 2021 Talapka, Kocsis, Marsi, Szarvas and Kisvárday.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Application of the mirror technique for block-face scanning electron microscopy.Brain Struct Funct. 2022 Jul;227(6):1933-1947. doi: 10.1007/s00429-022-02506-w. Epub 2022 May 28. Brain Struct Funct. 2022. PMID: 35643821 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of 5-hydroxytryptamine-immunoreactive boutons on alpha-motoneurons in the lumbar spinal cord of adult cats.J Comp Neurol. 1998 Mar 30;393(1):69-83. J Comp Neurol. 1998. PMID: 9520102
-
The section-Golgi impregnation procedure. 2. Immunocytochemical demonstration of glutamate decarboxylase in Golgi-impregnated neurons and in their afferent synaptic boutons in the visual cortex of the cat.Neuroscience. 1983 Jul;9(3):475-90. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90167-7. Neuroscience. 1983. PMID: 6194475
-
Fine structure of the ventral lateral nucleus (VL) of the Macaca mulatta thalamus: cell types and synaptology.J Comp Neurol. 1991 Dec 8;314(2):319-49. doi: 10.1002/cne.903140209. J Comp Neurol. 1991. PMID: 1723998
-
GABA distribution in a pain-modulating zone of trigeminal subnucleus interpolaris.Somatosens Res. 1988;5(3):205-17. doi: 10.3109/07367228809144627. Somatosens Res. 1988. PMID: 2895952 Review.
Cited by
-
Ultraplex microscopy: versatile highly-multiplexed molecular labeling and imaging across scale and resolution.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 19:2024.08.17.605585. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.17.605585. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39229092 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Application of the mirror technique for block-face scanning electron microscopy.Brain Struct Funct. 2022 Jul;227(6):1933-1947. doi: 10.1007/s00429-022-02506-w. Epub 2022 May 28. Brain Struct Funct. 2022. PMID: 35643821 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

