Identification, Biological Activities and Biosynthetic Pathway of Dendrobium Alkaloids
- PMID: 33959002
- PMCID: PMC8096351
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.605994
Identification, Biological Activities and Biosynthetic Pathway of Dendrobium Alkaloids
Abstract
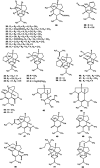
Dendrobium is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the Orchidaceae family with more than 1,400 species. Many Dendrobium species have been used as medicinal plants in several Asian countries for thousands of years. Alkaloids were reported as the major biological markers due to their complex chemical compositions and various types. In this review, we summarized the structural types of alkaloids, their pharmacological activities, as well as the mechanisms of biological activities. More than sixty alkaloids were isolated and identified from the Dendrobium genus. Moreover, the pharmacological effects of Dendrobium alkaloids as hepatic lipid and gluconeogenesis regulation, as neuroprotection, and as anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetes, and anti-virus factors were described. Besides, the total chemical synthesis of dendrobine is provided, while the biosynthetic pathway of dendrobine has been proposed based on the functions of associated genes. For applications of these invaluable herbs, more researches on the extraction of biological markers from compounds are needed. Further confirmation of the proposed biosynthetic pathways is anticipated as well.
Keywords: Dendrobium; alkaloids; anti-inflammatory; antitumor; biosynthetic pathway; mechanisms; orchidaceae.
Copyright © 2021 Mou, Zhao, Ye, Shi, Kennelly, Chen and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Begum S. A., Sahai M., Ray A. B., Gössinger E., Luzhetska M., Härle J., et al. (2010). Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products: Picrotoxanes. Vienna, Austria: Springer.
-
- Cakova V., Bonte F., Lobstein A. (2020). Dendrobium: Sources of Active Ingredients to Treat Age Related Pathologies. Aging Dis. 2, 827–849. 10.14336/AD.2017.0214. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chase M. W., Cameron K. M., Freudenstein J. V., Pridgeon A. M., Salazar G., Van den Berg C., et al. (2015). An Updated Classification of Orchidaceae. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 177, 151–174. 10.1111/boj.12234 - DOI
-
- Chen H., Li X., Xu Y., Lo K., Zheng H., Hu H., et al. (2018). Study on the Polar Extracts of Dendrobium Nobile, D. Officinale, D. Loddigesii, and Flickingeria Fimbriata: Metabolite Identification, Content Evaluation, and Bioactivity Assay. Molecules 23, 1185. 10.3390/molecules23051185 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen K. K., Chen A. L. (1935). The Alkaloid of Chin-Shih-Hu. J. Biol. Chem. 111, 653–658. 10.1016/s0021-9258(18)75010-2 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

