Blood Purification Techniques, Inflammatory Mediators and Mortality in COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 33959166
- PMCID: PMC8088142
Blood Purification Techniques, Inflammatory Mediators and Mortality in COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
Background: Inflammatory mediators are an important component in the pathophysiology of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This study aimed to assess the effects of reducing inflammatory mediators using hemoperfusion (HP) and continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) on the mortality of patients with COVID-19.
Materials and methods: Twelve patients with confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 were included. All patients had acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Patients were divided into three groups, namely, HP, CRRT and HP+CRRT. The primary outcome was mortality and the secondary outcomes were oxygenation and reduction in inflammatory mediators at the end of the study.
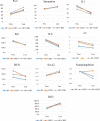
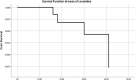
Results: Patients were not different at baseline in demographics, inflammatory cytokine levels, and the level of acute phase reactants. Half of the patients (3 out of 6) in the HP+CRRT group survived along with the survival of one patient (1 out of 2) in the HP group. All four patients in the CRRT group died. Serum creatinine (SCr), Interleukin-1 (IL1), Interleukin-6 (IL6), Interleukin-8 (IL8), partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2), O2 saturation (O2 sat), and hemodynamic parameters improved over time in HP+CRRT and CRRT groups, but no significant difference was observed in the HP group (All Ps > 0.05).
Conclusion: Combined HP and CRRT demonstrated the best result in terms of mortality, reduction of inflammatory mediators and oxygenation. Further investigations are needed to explore the role of HP+CRRT in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: ARDS; Acute respiratory distress syndrome; COVID-19; Continuous renal replacement therapy; Coronavirus disease 2019; Cytokine; Hemoperfusion; Inflammatory marker; Mortality; Oxygenation.
Copyright© 2020 National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests Not applicable.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
