3T DCE-MRI Radiomics Improves Predictive Models of Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
- PMID: 33959498
- PMCID: PMC8093630
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.630780
3T DCE-MRI Radiomics Improves Predictive Models of Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer
Abstract
Objectives: To test whether 3T MRI radiomics of breast malignant lesions improves the performance of predictive models of complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy when added to other clinical, histological and radiological information.
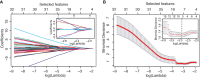
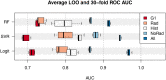
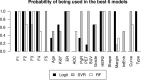
Methods: Women who consecutively had pre-neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) 3T DCE-MRI between January 2016 and October 2019 were retrospectively included in the study. 18F-FDG PET-CT and histological information obtained through lesion biopsy were also available. All patients underwent surgery and specimens were analyzed. Subjects were divided between complete responders (Pinder class 1i or 1ii) and non-complete responders to NAC. Geometric, first order or textural (higher order) radiomic features were extracted from pre-NAC MRI and feature reduction was performed. Five radiomic features were added to other available information to build predictive models of complete response to NAC using three different classifiers (logistic regression, support vector machines regression and random forest) and exploring the whole set of possible feature selections.
Results: The study population consisted of 20 complete responders and 40 non-complete responders. Models including MRI radiomic features consistently showed better performance compared to combinations of other clinical, histological and radiological information. The AUC (ROC analysis) of predictors that did not include radiomic features reached up to 0.89, while all three classifiers gave AUC higher than 0.90 with the inclusion of radiomic information (range: 0.91-0.98).
Conclusions: Radiomic features extracted from 3T DCE-MRI consistently improved predictive models of complete response to neo-adjuvant chemotherapy. However, further investigation is necessary before this information can be used for clinical decision making.
Keywords: DCE; MRI; breast cancer; machine learning; medical imaging; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; radiomics.
Copyright © 2021 Montemezzi, Benetti, Bisighin, Camera, Zerbato, Caumo, Fiorio, Zanelli, Zuffante and Cavedon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deep learning radiomic analysis of DCE-MRI combined with clinical characteristics predicts pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 5;12:1041142. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1041142. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36686755 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics for the pretreatment prediction of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy based on breast DCE-MRI.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 May 18;19(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13058-017-0846-1. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28521821 Free PMC article.
-
A delta-radiomic lymph node model using dynamic contrast enhanced MRI for the early prediction of axillary response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jan 5;23(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10496-5. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36604679 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-Treatment Prediction of Breast Cancer Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Using Intratumoral and Peritumoral Radiomics from T2-Weighted and Contrast-Enhanced T1-Weighted MRI.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Apr 30;17(9):1520. doi: 10.3390/cancers17091520. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361448 Free PMC article.
-
18F-FDG PET/CT radiomic predictors of pathologic complete response (pCR) to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020 May;47(5):1116-1126. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04684-3. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31982990
Cited by
-
Construction and validation of a personalized nomogram of ultrasound for pretreatment prediction of breast cancer patients sensitive to neoadjuvant chemotherapy.Br J Radiol. 2022 Dec 1;95(1140):20220626. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20220626. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Br J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 36378247 Free PMC article.
-
Respective contribution of baseline clinical data, tumour metabolism and tumour blood-flow in predicting pCR after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in HER2 and Triple Negative breast cancer.EJNMMI Res. 2024 Jul 4;14(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13550-024-01115-4. EJNMMI Res. 2024. PMID: 38965124 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of 18F-FDG PET/CT-based radiomics model for neoadjuvant chemotherapy efficacy in breast cancer: a multi-scanner/center study with external validation.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023 Jun;50(7):1869-1880. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06150-2. Epub 2023 Feb 20. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36808002
-
Analysis of the Value of Quantitative Features in Multimodal MRI Images to Construct a Radio-Omics Model for Breast Cancer Diagnosis.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2024 Jun 11;16:305-318. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S458036. eCollection 2024. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2024. PMID: 38895649 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting progression-free survival using dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging-based radiomics in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with nimotuzumab.Eur Radiol. 2025 Aug;35(8):5135-5145. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11433-3. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39953153
References
-
- Londero V, Bazzocchi M, Del Frate C, Puglisi F, Di Loreto C, Francescutti G, et al. . Locally advanced breast cancer: comparison of mammography, sonography and MR imaging in evaluation of residual disease in women receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur Radiol (2004) 14:1371–9. 10.1007/s00330-004-2246-z - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

