Enhanced siRNA Delivery and Selective Apoptosis Induction in H1299 Cancer Cells by Layer-by-Layer-Assembled Se Nanocomplexes: Toward More Efficient Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 33959633
- PMCID: PMC8093573
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.639184
Enhanced siRNA Delivery and Selective Apoptosis Induction in H1299 Cancer Cells by Layer-by-Layer-Assembled Se Nanocomplexes: Toward More Efficient Cancer Therapy
Abstract
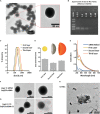
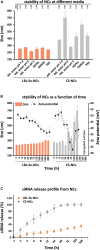
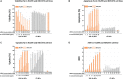
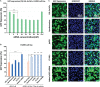
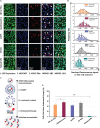
Nanotechnology has made an important contribution to oncology in recent years, especially for drug delivery. While many different nano-delivery systems have been suggested for cancer therapy, selenium nanoparticles (SeNPs) are particularly promising anticancer drug carriers as their core material offers interesting synergistic effects to cancer cells. Se compounds can exert cytotoxic effects by acting as pro-oxidants that alter cellular redox homeostasis, eventually leading to apoptosis induction in many kinds of cancer cells. Herein, we report on the design and synthesis of novel layer-by-layer Se-based nanocomplexes (LBL-Se-NCs) as carriers of small interfering RNA (siRNA) for combined gene silencing and apoptosis induction in cancer cells. The LBL-Se-NCs were prepared using a straightforward electrostatic assembly of siRNA and chitosan (CS) on the solid core of the SeNP. In this study, we started by investigating the colloidal stability and protection of the complexed siRNA. The results show that CS not only functioned as an anchoring layer for siRNA, but also provided colloidal stability for at least 20 days in different media when CS was applied as a third layer. The release study revealed that siRNA remained better associated with LBL-Se-NCs, with only a release of 35% after 7 days, as compared to CS-NCs with a siRNA release of 100% after 48 h, making the LBL nanocarrier an excellent candidate as an off-the-shelf formulation. When applied to H1299 cells, it was found that they can selectively induce around 32% apoptosis, while significantly less apoptosis (5.6%) was induced in NIH/3T3 normal cells. At the same time, they were capable of efficiently inducing siRNA downregulation (35%) without loss of activity 7 days post-synthesis. We conclude that LBL-Se-NCs are promising siRNA carriers with enhanced stability and with a dual mode of action against cancer cells.
Keywords: advanced drug delivery; apoptosis; cancer therapy; chitosan; nanomedicine; selenium nanoparticle; siRNA delivery.
Copyright © 2021 Sharifiaghdam, Shaabani, Sharifiaghdam, De Keersmaecker, De Rycke, De Smedt, Faridi-Majidi, Braeckmans and Fraire.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad M. Z., Rizwanullah M., Ahmad J., Alasmary M. Y., Akhter M. H., Abdel-Wahab B. A., et al. (2021). Progress in nanomedicine-based drug delivery in designing of chitosan nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 1–22
-
- Boroumand S., Safari M., Shaabani E., Shirza M., Faridi-Majidi R. (2019). Selenium nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and study of their cytotoxicity, antioxidant and antibacterial activity. Mater. Res. Express 6:0850d0858.
-
- Buyens K., De Smedt S. C., Braeckmans K., Demeester J., Peeters L., van Grunsven L. A., et al. (2012). Liposome based systems for systemic siRNA delivery: stability in blood sets the requirements for optimal carrier design. J. Control. Release 158 362–370. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2011.10.009 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

