Design and rationale of the EMPA-VISION trial: investigating the metabolic effects of empagliflozin in patients with heart failure
- PMID: 33960149
- PMCID: PMC8318430
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.13406
Design and rationale of the EMPA-VISION trial: investigating the metabolic effects of empagliflozin in patients with heart failure
Abstract
Aims: Despite substantial improvements over the last three decades, heart failure (HF) remains associated with a poor prognosis. The sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor empagliflozin demonstrated significant reductions of HF hospitalization in patients with HF independent of the presence or absence of type 2 diabetes mellitus in the EMPEROR-Reduced trial and cardiovascular mortality in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial. To further elucidate the mechanisms behind these positive outcomes, this study aims to determine the effects of empagliflozin treatment on cardiac energy metabolism and physiology using magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) and cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR).
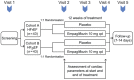
Methods and results: The EMPA-VISION trial is a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, mechanistic study. A maximum of 86 patients with HF with reduced ejection fraction (n = 43, Cohort A) or preserved ejection fraction (n = 43, Cohort B), with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus, will be enrolled. Participants will be randomized 1:1 to receive either 10 mg of empagliflozin or placebo for 12 weeks. Eligible patients will undergo cardiovascular magnetic resonance, resting and dobutamine stress MRS, echocardiograms, cardiopulmonary exercise tests, serum metabolomics, and quality of life questionnaires at baseline and after 12 weeks. The primary endpoint will be the change in resting phosphocreatine-to-adenosine triphosphate ratio, as measured by 31 Phosphorus-MRS.
Conclusions: EMPA-VISION is the first clinical trial assessing the effects of empagliflozin treatment on cardiac energy metabolism in human subjects in vivo. The results will shed light on the mechanistic action of empagliflozin in patients with HF and help to explain the results of the safety and efficacy outcome trials (EMPEROR-Reduced and EMPEROR-Preserved).
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03332212.
Keywords: 31P-MRS; Diabetes; Empagliflozin; Heart failure; SGLT2 inhibitors; Trial design.
© 2021 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
M.H., M.M., and S.N. are supported by an industrial grant provided by Boehringer Ingelheim. R.G. and H.N. are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. KG. The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR, or the Department of Health.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assessment of Cardiac Energy Metabolism, Function, and Physiology in Patients With Heart Failure Taking Empagliflozin: The Randomized, Controlled EMPA-VISION Trial.Circulation. 2023 May 30;147(22):1654-1669. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.062021. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Circulation. 2023. PMID: 37070436 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Rationale and Design of the EMPA-TROPISM Trial (ATRU-4): Are the "Cardiac Benefits" of Empagliflozin Independent of its Hypoglycemic Activity?Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2019 Feb;33(1):87-95. doi: 10.1007/s10557-018-06850-0. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2019. PMID: 30675708
-
Rationale and design of the EMPERIAL-Preserved and EMPERIAL-Reduced trials of empagliflozin in patients with chronic heart failure.Eur J Heart Fail. 2019 Jul;21(7):932-942. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.1486. Epub 2019 Jun 19. Eur J Heart Fail. 2019. PMID: 31218819 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of empagliflozin in patients with diabetes and heart failure.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2017 Feb;27(2):144-151. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2016.07.008. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2017. PMID: 27612553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reappraisal of the diuretic effect of empagliflozin in the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial: Comparison with classic diuretics.Diabetes Metab. 2016 Sep;42(4):224-33. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2016.05.006. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Diabetes Metab. 2016. PMID: 27291329 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Cardiac Energy Metabolism, Function, and Physiology in Patients With Heart Failure Taking Empagliflozin: The Randomized, Controlled EMPA-VISION Trial.Circulation. 2023 May 30;147(22):1654-1669. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.062021. Epub 2023 Apr 18. Circulation. 2023. PMID: 37070436 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Empagliflozin alleviates cardiac microvascular ischemia/reperfusion injury by maintaining myocardial mitochondrial homeostasis].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2013 Jul 20;43(7):1136-1144. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.07.10. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2013. PMID: 37488796 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors Improve Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction Outcomes by Reducing Edema and Congestion.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Apr 14;12(4):989. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12040989. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35454037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomic Profiling of the Effects of Dapagliflozin in Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction: DEFINE-HF.Circulation. 2022 Sep 13;146(11):808-818. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.060402. Epub 2022 May 23. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 35603596 Free PMC article.
-
SGLT2 Inhibition in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction - The New Frontier.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):1. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2401001. eCollection 2023 Jan. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39076855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr, Colvin MM, Drazner MH, Filippatos GS, Fonarow GC, Givertz MM, Hollenberg SM, Lindenfeld J, Masoudi FA, McBride PE, Peterson PN, Stevenson LW, Westlake C. 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA focused update of the 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Failure Society of America. J Am Coll Cardiol 2017; 70: 776–803. - PubMed
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, Falk V, Gonzalez‐Juanatey JR, Harjola VP, Jankowska EA, Jessup M, Linde C, Nihoyannopoulos P, Parissis JT, Pieske B, Riley JP, Rosano GMC, Ruilope LM, Ruschitzka F, Rutten FH, van der Meer P, Group ESCSD . 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J 2016; 37: 2129–2200. - PubMed
-
- Cook C, Cole G, Asaria P, Jabbour R, Francis DP. The annual global economic burden of heart failure. Int J Cardiol 2014; 171: 368–376. - PubMed
-
- Bursi F, Weston SA, Redfield MM, Jacobsen SJ, Pakhomov S, Nkomo VT, Meverden RA, Roger VL. Systolic and diastolic heart failure in the community. JAMA 2006; 296: 2209–2216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

