Facile synthesis of PEI-based crystalline templated mesoporous silica with molecular chirality for improved oral delivery of the poorly water-soluble drug
- PMID: 33960251
- PMCID: PMC8118497
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1912212
Facile synthesis of PEI-based crystalline templated mesoporous silica with molecular chirality for improved oral delivery of the poorly water-soluble drug
Abstract
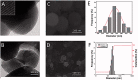
The aim of this study was to build up a novel chiral mesoporous silica called PEIs@TA-CMS through a facile biomimetic strategy and to explore its potential to serve as a drug carrier for improving the delivery efficiency of poorly water-soluble drug. PEIs@TA-CMS was synthesized by using a chiral crystalline complex associated of tartaric acid and polyethyleneimine (PEIs) as templates, scaffolds and catalysts. The structural features including morphology, size, pore structure and texture properties were systematacially studied. The results showed that PEIs@TA-CMS was monodispersed spherical nanoparticles in a uniformed diameter of 120-130 nm with well-developed pore structure (SBET: 1009.94 m2/g, pore size <2.21 nm). Then PEIs@TA-CMS was employed as nimodipine (NMP) carrier and compared with the drug carry ability of MCM41. After drug loading, NMP was effectively transformed from the crystalline state to an amorphous state due to the space confinement in mesopores. As expected, PEIs@TA-CMS had superiority in both drug loading and drug release compared to MCM41. It could incorporate NMP with high efficiency, and the dissolution-promoting effect of PEIs@TA-CMS was more obvious because of the unique interconnected curved pore channels. Meanwhile, PEIs@TA-CMS could significantly improve the oral adsorption of NMP to a satisfactory level, which showed approximately 3.26-fold higher in bioavailability, and could effectively prolong the survival time of mice on cerebral anoxia from 10.98 to 17.33 min.
Keywords: Biomimetic synthesis; chiral mesoporous silica; drug delivery; nimodipine; oral bioavailability.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures





Similar articles
-
Biomimetic synthesis and evaluation of histidine-derivative templated chiral mesoporous silica for improved oral delivery of the poorly water-soluble drug, nimodipine.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018 May 30;117:321-330. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2018.03.013. Epub 2018 Mar 9. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2018. PMID: 29530545
-
Biomimetic Synthesis and Evaluation of Interconnected Bimodal Mesostructured MSF@Poly(Ethyleneimine)s for Improved Drug Loading and Oral Adsorption of the Poorly Water-Soluble Drug, Ibuprofen.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Oct 5;15:7451-7468. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S272796. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 33116481 Free PMC article.
-
Novel scheme for rapid synthesis of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles (HMSNs) and their application as an efficient delivery carrier for oral bioavailability improvement of poorly water-soluble BCS type II drugs.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019 Apr 1;176:185-193. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.01.004. Epub 2019 Jan 2. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019. PMID: 30616109
-
Mesoporous Silica Molecular Sieve based Nanocarriers: Transpiring Drug Dissolution Research.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(3):467-480. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666161026162005. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 27784249 Review.
-
Mesoporous silica formulation strategies for drug dissolution enhancement: a review.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016;13(1):93-108. doi: 10.1517/17425247.2016.1100165. Epub 2015 Nov 7. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 26549623 Review.
Cited by
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles with chiral pattern topological structure function as "antiskid tires" on the intestinal mucosa to facilitate oral drugs delivery.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023 Mar;18(2):100795. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2023.100795. Epub 2023 Feb 25. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 37008734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed N, Näsman P, Wahlgren NG. (2000). Effect of intravenous nimodipine on blood pressure and outcome after acute stroke. Stroke 31:1250–5. - PubMed
-
- Benoit DSW, Nuttelman CR, Collins SD, Anseth KS. (2006). Synthesis and characterization of a fluvastatin-releasing hydrogel delivery system to modulate hmsc differentiation and function for bone regeneration. Biomaterials 27:6102–10. - PubMed
-
- Che S, Liu Z, Ohsuna T, et al. (2004). Synthesis and characterization of chiral mesoporous silica. Nature 429:281–4. - PubMed
-
- Chen XQ, Ziemba T, Huang C, et al. (2018). Oral delivery of highly lipophilic poorly water-soluble drugs: self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS) to improve oral absorption and enable high dose toxicology studies of a CETP inhibitor in preclinical species. J Pharm Sci 107:1352–60. - PubMed
-
- Chiappetta DA, Sosnik A. (2007). Poly(ethylene oxide)-poly(propylene oxide) block copolymer micelles as drug delivery agents: improved hydrosolubility, stability and bioavailability of drugs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 66:303–17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
