Objective measurements for upper airway obstruction in infants with Robin sequence: what are we measuring? A systematic review
- PMID: 33960296
- PMCID: PMC8656914
- DOI: 10.5664/jcsm.9394
Objective measurements for upper airway obstruction in infants with Robin sequence: what are we measuring? A systematic review
Abstract
Study objectives: Identifying optimal treatment for infants with Robin sequence (RS) is challenging due to substantial variability in the presentation of upper airway obstruction (UAO) in this population. Objective assessments of UAO and treatments are not standardized. A systematic review of objective measures of UAO was conducted as a step toward evidence-based clinical decision-making for RS.
Methods: A literature search was performed in the PubMed and Embase databases (1990-2020) following PRISMA guidelines. Articles reporting on RS and UAO treatment were included if the following objective measures were studied: oximetry, polysomnography, and blood gas. Quality was appraised by the methodological index for nonrandomized studies (range: 0-24).
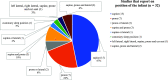
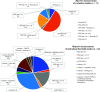
Results: A total of 91 articles met the inclusion criteria. The mean methodological index for nonrandomized studies score was 7.1 (range: 3-14). Polysomnography was most frequently used (76%) followed by oximetry (20%) and blood gas (11%). Sleep position of the infant was reported in 35% of studies, with supine position most frequently, and monitoring time in 42%, including overnight recordings, in more than half. Of 71 studies that evaluated UAO interventions, the majority used polysomnography (90%), of which 61% did not specify the polysomnography technique. Reported polysomnography metrics included oxygen saturation (61%), apnea-hypopnea index (52%), carbon dioxide levels (31%), obstructive apnea-hypopnea index (27%), and oxygen desaturation index (16%). Only 42 studies reported indications for UAO intervention, with oximetry and polysomnography thresholds used equally (both 40%). In total, 34 distinct indications for treatment were identified.
Conclusions: This systematic review demonstrates a lack of standardization, interpretation, and reporting of assessment and treatment indications for UAO in RS. An international, multidisciplinary consensus protocol is needed to guide clinicians on optimal UAO assessment in RS.
Citation: Logjes RJH, MacLean JE, de Cort NW, et al. Objective measurements for upper airway obstruction in infants with Robin sequence: what are we measuring? A systematic review. J Clin Sleep Med. 2021;17(8):1717-1729.
Keywords: apnea-hypopnea index; blood gas; carbon dioxide; obstructive apnea-hypopnea index; obstructive sleep apnea; oximetry; oxygen desaturation index; oxygen saturation; polysomnography.
© 2021 American Academy of Sleep Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differences in analysis and treatment of upper airway obstruction in Robin sequence across different countries in Europe.Eur J Pediatr. 2023 Mar;182(3):1271-1280. doi: 10.1007/s00431-022-04781-5. Epub 2023 Jan 12. Eur J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36633656
-
Evaluation of upper airway obstruction in infants with Pierre Robin sequence and the role of polysomnography--Review of current evidence.Paediatr Respir Rev. 2016 Jan;17:80-7. doi: 10.1016/j.prrv.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2016. PMID: 26563513 Review.
-
Gas exchange parameters for the prediction of obstructive sleep apnea in infants.J Clin Sleep Med. 2024 Jul 1;20(7):1059-1067. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.11064. J Clin Sleep Med. 2024. PMID: 38372169 Free PMC article.
-
The challenge of assessing upper airway obstruction severity in infants with Robin Sequence.Sleep Med. 2025 Aug;132:106535. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2025.106535. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Sleep Med. 2025. PMID: 40315670
-
The Tübingen palatal plate approach to Robin sequence: Summary of current evidence.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019 Nov;47(11):1699-1705. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2019.08.002. Epub 2019 Aug 20. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31477439 Review.
Cited by
-
Differences in analysis and treatment of upper airway obstruction in Robin sequence across different countries in Europe.Eur J Pediatr. 2023 Mar;182(3):1271-1280. doi: 10.1007/s00431-022-04781-5. Epub 2023 Jan 12. Eur J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 36633656
-
Robin Sequence: From Dilemmas to Developing an Adaptable Standardized Stepwise Approach.Acta Paediatr. 2025 Aug;114(8):1760-1777. doi: 10.1111/apa.70028. Epub 2025 Feb 13. Acta Paediatr. 2025. PMID: 39945272 Free PMC article.
-
Spectrum of Disease in Hospitalized Newborns with Congenital Micrognathia: A Cohort of 3,236 Infants at North American Tertiary-Care Intensive Care Units.J Pediatr. 2024 Feb;265:113799. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2023.113799. Epub 2023 Oct 23. J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 37879601 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Surgical Respiratory Management in Relation to Feeding and Growth in Patients with Robin Sequence; a Prospective Longitudinal Study.Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2023 Sep 20;62(1):10556656231199840. doi: 10.1177/10556656231199840. Online ahead of print. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2023. PMID: 37728101 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and Early Management of Robin Sequence.Children (Basel). 2024 Sep 6;11(9):1094. doi: 10.3390/children11091094. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334626 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Robin P . La chute de la base de la langue considérée comme une nouvelle cause de gêne dans la respiration naso-pharyngienne . Bull Acad Med Paris . 1923. ; 89 : 37 – 41 .
-
- Paes EC , van Nunen DPF , Basart H , et al. . Birth prevalence of Robin sequence in the Netherlands from 2000-2010: a retrospective population-based study in a large Dutch cohort and review of the literature . Am J Med Genet A . 2015. ; 167A ( 9 ): 1972 – 1982 . - PubMed
-
- Logjes RJH , Breugem CC , Van Haaften G , et al. . The ontogeny of Robin sequence . Am J Med Genet A . 2018. ; 176 ( 6 ): 1349 – 1368 . - PubMed
-
- Tan TY , Kilpatrick N , Farlie PG . Developmental and genetic perspectives on Pierre Robin sequence . Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet . 2013. ; 163C ( 4 ): 295 – 305 . - PubMed
-
- St-Hilaire H , Buchbinder D . Maxillofacial pathology and management of Pierre Robin sequence . Otolaryngol Clin North Am . 2000. ; 33 ( 6 ): 1241 – 1256 . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

