Efficacy and safety of biophenol-rich nutraceuticals in adults with inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases or irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33960587
- PMCID: PMC9290971
- DOI: 10.1111/1747-0080.12672
Efficacy and safety of biophenol-rich nutraceuticals in adults with inflammatory gastrointestinal diseases or irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Aim: Biophenol-rich nutraceuticals may be an adjuvant treatment for Crohn's disease (CD), ulcerative colitis (UC), symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease (SUDD), and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to determine the efficacy and safety of biophenol-rich nutraceutical supplementation on CD, UC, SUDD, and IBS on gastrointestinal symptoms (GIS), quality of life (QoL), inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers, and adverse events compared to usual care or placebo.
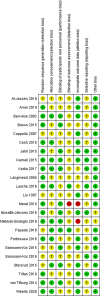
Methods: PubMed, Embase, CINAHL, and CENTRAL were searched for randomised controlled trials until 27 April 2020. Outcomes were GIS, inflammatory and oxidative stress markers, QoL, and adverse events. The Cochrane Risk of Bias tool and GRADE were used to appraise studies. Data were pooled using Revman.
Results: Twenty-three trials in CD, UC, and IBS patients were included. Compared with placebo, biophenol-rich nutraceuticals improved GIS (SMD: 0.43 [95%CI: 0.22, 0.63]; GRADE: very low) in UC, CD, and IBS participants. In UC and CD participants, biophenol-rich nutraceuticals improved CRP by 1.6 mg/L [95%CI:0.08, 3.11; GRADE: low], malondialdehyde by 1 mmol/L [95%CI:0.55, 1.38; GRADE: low]; but only resveratrol improved QoL (SMD: -0.84 [95%CI: -1.24, -0.44; GRADE: high). Resveratrol (for UC and CD participants) and peppermint oil (for IBS participants) had greater certainty in the evidence for improving GIS and QoL (GRADE: moderate to high). There was no effect on adverse events (P > .05).
Conclusions: Biophenol-rich nutraceuticals may be an effective and safe adjuvant treatment for the management of CD, UC, and IBS; with higher certainty of evidence for resveratrol for UC and CD and peppermint oil for IBS.
Keywords: Crohn disease; diverticular diseases; inflammatory bowel diseases; irritable bowel syndrome; polyphenols; ulcerative colitis.
© 2021 The Authors. Nutrition & Dietetics published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Dietitians Australia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

