The miR164-GhCUC2-GhBRC1 module regulates plant architecture through abscisic acid in cotton
- PMID: 33960609
- PMCID: PMC8428825
- DOI: 10.1111/pbi.13599
The miR164-GhCUC2-GhBRC1 module regulates plant architecture through abscisic acid in cotton
Abstract
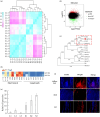
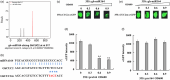
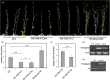
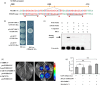
Branching determines cotton architecture and production, but the underlying regulatory mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we report that the miR164-GhCUC2 (CUP-SHAPED COTYLEDON2) module regulates lateral shoot development in cotton and Arabidopsis. We generated OE-GhCUC2m (overexpression GhCUC2m) and STTM164 (short tandem target mimic RNA of miR164) lines in cotton and heterologous expression lines for gh-miR164, GhCUC2 and GhCUC2m in Arabidopsis to study the mechanisms controlling lateral branching. GhCUC2m overexpression resulted in a short-branch phenotype similar to STTM164. In addition, heterologous expression of GhCUC2m led to decreased number and length of branches compared with wild type, opposite to the effects of the OE-gh-pre164 line in Arabidopsis. GhCUC2 interacted with GhBRC1 and exhibited similar negative regulation of branching. Overexpression of GhBRC1 in the brc1-2 mutant partially rescued the mutant phenotype and decreased branch number. GhBRC1 directly bound to the NCED1 promoter and activated its transcription, leading to local abscisic acid (ABA) accumulation and response. Mutation of the NCED1 promoter disrupted activation by GhBRC1. This finding demonstrates a direct relationship between BRC1 and ABA signalling and places ABA downstream of BRC1 in the control of branching development. The miR164-GhCUC2-GhBRC1-GhNCED1 module provides a clear regulatory axis for ABA signalling to control plant architecture.
Keywords: GhBRC1; GhCUC2; ABA; lateral branch; miR164.
© 2021 The Authors. Plant Biotechnology Journal published by Society for Experimental Biology and The Association of Applied Biologists and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
GhSBI1, a CUP-SHAPED COTYLEDON 2 homologue, modulates branch internode elongation in cotton.Plant Biotechnol J. 2024 Nov;22(11):3175-3193. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14439. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Plant Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 39058556 Free PMC article.
-
GhTIE1 Regulates Branching Through Modulating the Transcriptional Activity of TCPs in Cotton and Arabidopsis.Front Plant Sci. 2019 Oct 28;10:1348. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01348. eCollection 2019. Front Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31719830 Free PMC article.
-
GhWRKY21 regulates ABA-mediated drought tolerance by fine-tuning the expression of GhHAB in cotton.Plant Cell Rep. 2021 Nov;40(11):2135-2150. doi: 10.1007/s00299-020-02590-4. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Plant Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 32888081
-
The role of peu-miR164 and its target PeNAC genes in response to abiotic stress in Populus euphratica.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2017 Jun;115:418-438. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.04.009. Epub 2017 Apr 8. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28445829
-
A novel NAP member GhNAP is involved in leaf senescence in Gossypium hirsutum.J Exp Bot. 2015 Aug;66(15):4669-82. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv240. Epub 2015 May 18. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 25991739 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The 4Fs of cotton: genome editing of cotton for fiber, food, feed, and fuel to achieve zero hunger.Front Genome Ed. 2024 Sep 12;6:1401088. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2024.1401088. eCollection 2024. Front Genome Ed. 2024. PMID: 39328243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Current Progresses in the Genes and Networks Regulating Cotton Plant Architecture.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 9;13:882583. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.882583. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35755647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LncRNA81246 regulates resistance against tea leaf spot by interrupting the miR164d-mediated degradation of NAC1.Plant J. 2025 Jan;121(1):e17173. doi: 10.1111/tpj.17173. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Plant J. 2025. PMID: 39590921 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclanilide Induces Lateral Bud Outgrowth by Modulating Cytokinin Biosynthesis and Signalling Pathways in Apple Identified via Transcriptome Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 6;23(2):581. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020581. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054767 Free PMC article.
-
A deletion/duplication in the Ligon lintless-2 locus induces siRNAs that inhibit cotton fiber cell elongation.Plant Physiol. 2022 Oct 27;190(3):1792-1805. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac384. Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35997586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aida, M. and Tasaka, M. (2006) Genetic control of shoot organ boundaries. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 9, 72–77. - PubMed
-
- Alice, V. , Priyanka, M. , Adrian, R. , Ulla, N. , Karin, L. and Maria, C. (2020) Vernalization shapes shoot architecture and ensures the maintenance of dormant buds in the perennial Arabis alpina . New Phytol. 227, 99–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

