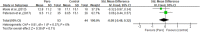How PARO can help older people in elderly care facilities: A systematic review of RCT
- PMID: 33960698
- PMCID: PMC9292779
- DOI: 10.1111/2047-3095.12327
How PARO can help older people in elderly care facilities: A systematic review of RCT
Abstract
Purpose: This review aims to systematically evaluate the effects of Paro on older adults and provide a stronger basis for the rational application of Paro in aged care facilities.
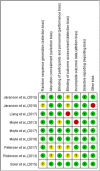
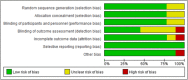
Methods: Articles published between January 2003 and January 2020 via five databases (PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), and Chinese database SinoMed) were searched. The Cochrane collaboration tool for randomized controlled trials was used to assess the quality of all included studies.
Results: Nine articles were included in this systematic review. All articles were summarized according to three themes: quality of life, and biopsychological conditions, and drug usage.
Conclusions: The review demonstrated that interaction with Paro can be beneficial for improving quality of life (QOL), biopsychological conditions, and reducing psychotropic and pain medical usage. Since the differences of the study design and low to moderate quality of these studies, however, we should be cautious to make positive comments on the role of Paro.
Implications of nursing practice: The implications of Paro in aged care facilities have positive effects on nursing outcomes. This review helps caregivers understand the advantages and disadvantages of care robots, and promotes the integration of intelligent technology and manual services in nursing practice.
Keywords: Paro; aged care facilities.
© 2021 The Authors. International Journal of Nursing Knowledge published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of NANDA International.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there if no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
References
-
- Barker, S. B. , Pandurangi, A. K. , & Best, A. M. (2003). Effects of animal‐assisted therapy on patients' anxiety, fear, and depression before ECT. The Journal of ECT, 19(1), 38–44.Retrieved from https://journals.lww.com/ectjournal/Fulltext/2003/03000/Effects_of_Anima... - PubMed
-
- Broekens, J. , Heerink, M. , & Rosendal, H. (2009). Assistive social robots in elderly care: A review. Gerontechnology, 8(2), 94–103.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials