Preoperative Alpha-Fetoprotein Has No Prognostic Role in Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Non-Cirrhotic Patients After Surgical Resection
- PMID: 33960936
- PMCID: PMC8975432
- DOI: 10.5152/tjg.2020.20156
Preoperative Alpha-Fetoprotein Has No Prognostic Role in Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Non-Cirrhotic Patients After Surgical Resection
Abstract
Background: Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) has been widely used as a tumor marker in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with cirrhosis. However, a large number of HCC patients are diagnosed without cirrhosis, and the prognostic capability of AFP was unclear in HCC patients without cirrhosis. Our purpose was to investigate the prognostic efficiency of AFP in patients with non-cirrhosis, single, and small HCC who were treated with surgical resection.
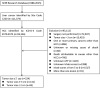
Methods: Among the 111 374 liver cancer patients included in the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results database, we selected 224 patients without cirrhosis with a single HCC ≤3 cm in diameter who were identified at diagnosis and treated with surgical resection. The AFP test results were recorded as AFP-positive and AFP-negative levels.
Results: Kaplan-Meier method showed that there was no significant survival difference between the AFP-positive and AFP-negative groups (P = .566). The same results were found in the subgroups of patients with tumor size ≤2 cm and 2-3 cm (P = .710 and .687, respectively). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis showed that AFP had inadequate accuracy to discriminate survivors and deceased patients in subgroups of patients with tumor size ≤3 cm, 2-3 cm, or ≤2 cm (area under the ROC curve = 0.449, 0.458, 0.443; 95% confidence interval = 0.366-0.533, 0.346-0.571, 0.317-0.569, respectively).
Conclusion: AFP levels have no predictive value in well-compensated non-cirrhosis patients with single, small HCC (≤3 cm) treated with surgical resection for curative intent.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Alpha-fetoprotein has no prognostic role in small hepatocellular carcinoma identified during surveillance in compensated cirrhosis.Hepatology. 2012 Oct;56(4):1371-9. doi: 10.1002/hep.25814. Hepatology. 2012. PMID: 22535689
-
Preoperative serum α-fetoprotein and prognosis after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma.Br J Surg. 2016 May;103(6):716-724. doi: 10.1002/bjs.10093. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Br J Surg. 2016. PMID: 26996727
-
Clinical Significance of Alpha-Fetoprotein in Alpha-Fetoprotein Negative Hepatocellular Carcinoma Underwent Curative Resection.Dig Dis Sci. 2021 Dec;66(12):4545-4556. doi: 10.1007/s10620-020-06797-z. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Dig Dis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33723698 Free PMC article.
-
[A new prognostic score system of hepatocellular carcinoma following hepatectomy].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017 Dec 23;39(12):903-909. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2017.12.005. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 29262506 Chinese.
-
Surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients: Current knowledge and future directions.Hepatol Forum. 2020 Sep 21;1(3):112-118. doi: 10.14744/hf.2020.2020.0003. eCollection 2020 Sep. Hepatol Forum. 2020. PMID: 35949723 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
