Luminescence lifetime imaging of three-dimensional biological objects
- PMID: 33961054
- PMCID: PMC8126452
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.254763
Luminescence lifetime imaging of three-dimensional biological objects
Abstract
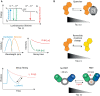
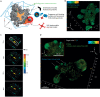
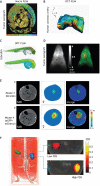
A major focus of current biological studies is to fill the knowledge gaps between cell, tissue and organism scales. To this end, a wide array of contemporary optical analytical tools enable multiparameter quantitative imaging of live and fixed cells, three-dimensional (3D) systems, tissues, organs and organisms in the context of their complex spatiotemporal biological and molecular features. In particular, the modalities of luminescence lifetime imaging, comprising fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLI) and phosphorescence lifetime imaging microscopy (PLIM), in synergy with Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) assays, provide a wealth of information. On the application side, the luminescence lifetime of endogenous molecules inside cells and tissues, overexpressed fluorescent protein fusion biosensor constructs or probes delivered externally provide molecular insights at multiple scales into protein-protein interaction networks, cellular metabolism, dynamics of molecular oxygen and hypoxia, physiologically important ions, and other physical and physiological parameters. Luminescence lifetime imaging offers a unique window into the physiological and structural environment of cells and tissues, enabling a new level of functional and molecular analysis in addition to providing 3D spatially resolved and longitudinal measurements that can range from microscopic to macroscopic scale. We provide an overview of luminescence lifetime imaging and summarize key biological applications from cells and tissues to organisms.
Keywords: Fluorescence lifetime; Imaging; Three dimensional.
© 2021. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Persistent luminescence nanoprobe for biosensing and lifetime imaging of cell apoptosis via time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy transfer.Biomaterials. 2015 Oct;67:323-34. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.07.037. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 26232881
-
Quantitative Imaging of Genetically Encoded Fluorescence Lifetime Biosensors.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Oct 19;13(10):939. doi: 10.3390/bios13100939. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo O2 imaging in hepatic tissues by phosphorescence lifetime imaging microscopy using Ir(III) complexes as intracellular probes.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 3;10(1):21053. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76878-6. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33273499 Free PMC article.
-
Förster resonance energy transfer biosensors for fluorescence and time-gated luminescence analysis of rac1 activity.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 28;12(1):5291. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09364-w. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35351946 Free PMC article.
-
Luminescence Probes in Bio-Applications: From Principle to Practice.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Jul 8;14(7):333. doi: 10.3390/bios14070333. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39056609 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deep learning in macroscopic diffuse optical imaging.J Biomed Opt. 2022 Feb;27(2):020901. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.27.2.020901. J Biomed Opt. 2022. PMID: 35218169 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Technique for Fluorescence Lifetime Tomography.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 16:2024.09.19.613888. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.19.613888. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39345436 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Non-Mass Spectrometric Targeted Single-Cell Metabolomics.Trends Analyt Chem. 2023 Nov;168:117300. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2023.117300. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Trends Analyt Chem. 2023. PMID: 37840599 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence Intensity and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopies (FLIM) of Cell Differentiation in the Small Intestinal Organoids Using Cholera Toxin.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2650:171-195. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3076-1_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37310632
-
[Research progress on the fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based polymer micelles as drug carriers].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Oct 25;39(5):1022-1032. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202111040. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36310492 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

