β-d-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells
- PMID: 33961695
- PMCID: PMC8136050
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiab247
β-d-N4-hydroxycytidine Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Through Lethal Mutagenesis But Is Also Mutagenic To Mammalian Cells
Abstract
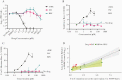
Mutagenic ribonucleosides can act as broad-based antiviral agents. They are metabolized to the active ribonucleoside triphosphate form and concentrate in genomes of RNA viruses during viral replication. β-d-N4-hydroxycytidine (NHC, initial metabolite of molnupiravir) is >100-fold more active than ribavirin or favipiravir against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), with antiviral activity correlated to the level of mutagenesis in virion RNA. However, NHC also displays host mutational activity in an animal cell culture assay, consistent with RNA and DNA precursors sharing a common intermediate of a ribonucleoside diphosphate. These results indicate highly active mutagenic ribonucleosides may hold risk for the host.
Keywords: NHC; SARS-CoV-2; molnupiravir; mutagenicity.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Letter to the Editor in Response to Zhou et al.J Infect Dis. 2021 Oct 28;224(8):1442-1443. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab362. J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34251432 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
COVID antiviral pills: what scientists still want to know.Nature. 2021 Nov;599(7885):358-359. doi: 10.1038/d41586-021-03074-5. Nature. 2021. PMID: 34759341 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

