Proposal of novel natural inhibitors of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 main protease: Molecular docking and ab initio fragment molecular orbital calculations
- PMID: 33962341
- PMCID: PMC8084281
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpc.2021.106608
Proposal of novel natural inhibitors of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 main protease: Molecular docking and ab initio fragment molecular orbital calculations
Abstract
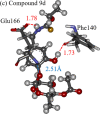
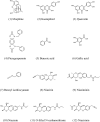
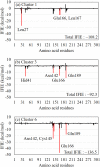
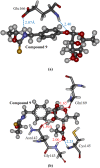
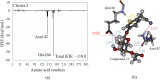
This paper proposes natural drug candidate compounds for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We investigated the binding properties between the compounds in the Moringa oleifera plant and the main protease (Mpro) of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 using molecular docking and ab initio fragment molecular orbital calculations. Among the 12 compounds, niaziminin was found to bind the strongest to Mpro. We furthermore proposed novel compounds based on niaziminin and investigated their binding properties to Mpro. The results reveal that the introduction of a hydroxyl group into niaziminin enhances its binding affinity to Mpro. These niaziminin derivatives can be promising candidate drugs for the treatment of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Fragment molecular orbital; In silico drug design; Main protease; Molecular docking; Molecular simulation; Moringa oleifera; Natural product; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Pal M., Kerorsa G.B., Kandi V.A. Knowledge update on SARS-Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2)/COVID-19 and its global public health implications. Am. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2020;8:23–27.
-
- Motiwale M., Yadav N.S., Kumar S., et al. Finding potent inhibitors for COVID-19 main protease (Mpro): an in silico approach using SARS-CoV-3CL protease inhibitors for combating CORONA. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020;7:1–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

