A new lesser metatarsophalangeal joint replacement arthroplasty design - in vitro and cadaver studies
- PMID: 33962604
- PMCID: PMC8106176
- DOI: 10.1186/s12891-021-04257-x
A new lesser metatarsophalangeal joint replacement arthroplasty design - in vitro and cadaver studies
Abstract
Background: Isolated degenerative joint disease and/or Freiberg's infraction of the lesser metatarsophalangeal joint, although not frequent may become debilitating in the younger individual. Currently, once conservative management fails, the mainstay of treatment is debridement and excision-interposition arthroplasty. Replacement arthroplasty has been ineffective in the long term as the joints are subject to severe repetitive fatigue loading over small articulating surfaces through a wide range of motion. This is an in vitro and cadaver study of a new design replacement arthroplasty developed by the senior author. The aim of this study is to evaluate this novel replacement arthroplasty of the lesser metatarsophalangeal joint in a laboratory setting and cadaver implantation.
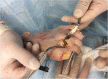
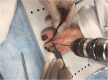
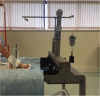
Methods: This three-component mobile bearing device is made of titanium and high density polyethylene which evolved over 4 years. It was subjected to 5,000,000 cycles in a laboratory under physiological and excessive forces to assess resistance to fatigue failure and wear pattern of the polyethylene liner. Following these tests, it was implanted in 15 fresh frozen cadavers at various stages of its development, during which the surgical technique was perfected. Range of motion and stability was tested using custom made instrumentation in four cadavers. The implant was inserted in a further two cadavers by an independent foot and ankle surgeon to check reproducibility.
Results: The device showed almost no signs of wear or surface deformation under physiological forces. The surgical technique was found to be simple and reproducible in the cadaver trial. The average dorsiflexion was 28.5° and 28.9° pre- and post-implant respectively. The average plantar flexion was 33.8° and 20.8° pre- and post- implant respectively. The joints were stable both pre- and post-operatively. Post-operative stability was objectively assessed for dorsal displacement and dorsiflexion using a 5 kgf (49 N) and was found to be excellent.
Conclusion: This novel lesser metatarsophalangeal joint replacement arthroplasty has been developed as an option in the surgical treatment of symptomatic degenerative joint disease and/or Freiberg's infraction resistant to conservative treatment. The implant was found to be durable and resistant to wear in the laboratory testing. The cadaver studies have shown it to require minimal specialized instrumentation with good surgical reproducibility. This proof of concept study is the basis for clinical trials.
Keywords: Arthritis; Cadaver studies; Freiberg’s infraction; Lesser metatarsophalangeal joint; New design; Replacement arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Each author certifies that he has no commercial associations that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article.
Figures












References
-
- Lavery L, Harkless LJTJ. The interpositional arthroplasty procedure in treatment of degenerative arthritis of the second metatarsophalangeal joint. J Foot Surg. 1992;31(6):590–594. - PubMed
-
- Enriquez Castro JA, Guevara Hernandez G, Estevez DG. Interposition arthroplasty as treatment of osteochondritis of the second metatarsal head. A case report. Acta Ortop Mex. 2008;22(4):259–262. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

