Variability of risk factors and diabetes complications
- PMID: 33962641
- PMCID: PMC8106175
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-021-01289-4
Variability of risk factors and diabetes complications
Abstract
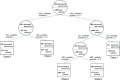
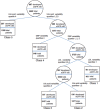
Several studies suggest that, together with glucose variability, the variability of other risk factors, as blood pressure, plasma lipids, heart rate, body weight, and serum uric acid, might play a role in the development of diabetes complications. Moreover, the variability of each risk factor, when contemporarily present, may have additive effects. However, the question is whether variability is causal or a marker. Evidence shows that the quality of care and the attainment of the target impact on the variability of all risk factors. On the other hand, for some of them causality may be considered. Although specific studies are still lacking, it should be useful checking the variability of a risk factor, together with its magnitude out of the normal range, in clinical practice. This can lead to an improvement of the quality of care, which, in turn, could further hesitate in an improvement of risk factors variability.
Keywords: Blood pressure variability; Body weight variability; Cardiovascular complications; Diabetes mellitus; Glucose variability; Heart rate variability; Lipids variability; Microvascular complications; Oxidative stress; Uric acid variability.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors do not have conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

