Asymptomatic COVID-19 re-infection in a Japanese male by elevated half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of neutralizing antibodies
- PMID: 33962861
- PMCID: PMC8064832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jiac.2021.04.017
Asymptomatic COVID-19 re-infection in a Japanese male by elevated half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of neutralizing antibodies
Abstract
Introduction: "Re-infection" with COVID-19 is a growing concern; re-infection cases have reported worldwide. However, the clinical characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 re-infection, including the levels and role of anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein IgG antibodies and the half-maximal concentration (IC50) of neutralizing antibodies remain unknown.
Methods: Both the epidemiological and clinical information has been collected during two episodes of COVID-19 in a patient. Laboratory results, including RT-PCR, Ct values, anti-SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein IgG antibodies, and the IC50 of neutralizing antibodies levels were analyzed on the patient.
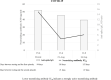
Results: The patient was a 58-year-old man who developed moderate COVID-19 pneumonia with oxygen demand (cannula 2 L/min) in the first episode. By day 30, he recuperated and was discharged after testing negative for SARS-CoV-2. After two and a half months, his three family members showed COVID-19 symptoms and tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. He tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 once again and was asymptomatic (the second episode). The IC50 of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 greatly increased from 50.0 μg/mL (after the first episode) to 14.8 μg/mL (after the second episode), and remained strongly reactive (20.1 μl/mL) after 47 days of the second episode.
Conclusions: Epidemiological, clinical, and serological analyses confirmed that the patient had re-infection instead of persistent viral shedding from first infection. Our results suggest that SARS-CoV-2 re-infection may manifest as asymptomatic with increased neutralizing antibody levels. Further studies such as the virus characteristics, immunology, and epidemiology on SARS-CoV-2 re-infection are needed.
Keywords: Anti-Spike protein IgG antibody; COVID-19; Neutralizing antibody; Re-infection; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2021 Japanese Society of Chemotherapy and The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest regarding this study.
Figures

References
-
- WHO, World Health Organization Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) weekly epidemiological update and weekly operational update. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio... (Accessed March 19, 2021)
-
- To K.K., Tsang O.T., Leung W.S., Tam A.R., Wu T.C., Lung D.C., et al. Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples and serum antibody responses during infection by SARS-CoV-2: an observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20:565–574. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30196-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

