Delivering clinical trials at home: protocol, design and implementation of a direct-to-family paediatric lupus trial
- PMID: 33963084
- PMCID: PMC8108689
- DOI: 10.1136/lupus-2021-000494
Delivering clinical trials at home: protocol, design and implementation of a direct-to-family paediatric lupus trial
Abstract
Introduction: Direct-to-family clinical trials efficiently provide data while reducing the participation burden for children and their families. Although these trials can offer significant advantages over traditional clinical trials, the process of designing and implementing direct-to-family studies is poorly defined, especially in children with rheumatic disease. This paper provides lessons learnt from the design and implementation of a self-controlled, direct-to-family pilot trial aimed to evaluate the effects of a medication management device on adherence to hydroxychloroquine in paediatric SLE.
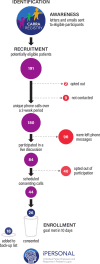
Methods: Several design features accommodate a direct-to-family approach. Participants meeting eligibility criteria from across the USA were identified a priori through a disease registry, and all outcome data are collected remotely. The primary outcome (medication adherence) is evaluated using electronic medication event-monitoring, plasma drug levels, patient questionnaires and pill counts. Secondary and exploratory endpoints include (1) lupus disease activity measured by a remote SLE Disease Activity Index examination and the Systemic Lupus Activity Questionnaire; and (2) hydroxychloroquine pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Recruitment of the initial target of 20 participants was achieved within 10 days. Due to initial recruitment success, enrolment was increased to 26 participants. Additional participants who were interested were placed on a waiting list in case of dropouts during the study.
Discussion and dissemination: Direct-to-family trials offer several advantages but present unique challenges. Lessons learnt from the protocol development, design, and implementation of this trial will inform future direct-to-family trials for children and adults with rheumatic diseases. Additionally, the data collected remotely in this trial will provide critical information regarding the accuracy of teleresearch in lupus, the impact of adherence to hydroxychloroquine on disease activity and a pharmacokinetic analysis to inform paediatric-specific dosing of hydroxychloroquine.
Trial registration number: ClinicalTrials.gov Registry (NCT04358302).
Keywords: antirheumatic agents; autoimmune diseases; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RR’s spouse has current or prior employment and/or stock ownership in Merck & Co, and Biogen. LES has received consulting fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria from UCB, Sanofi, Bristol Myers Squibb and Sobi (less than $10 000 each), and research support from CARRA. LES serves on the Data and Safety Monitoring Board for Sanofi (sarilumab). Sanofi is a maker of hydroxychloroquine. LES is a former board chair and currently sits on the Registry and Research Oversight Committee for CARRA. CPH receives salary support for research from sponsors for drug development in adults and children (https://dcri.org/about-us/conflict-of-interest/). SB consults for UCB.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- K23 AR075874/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- K24 AI143971/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN275201000003C/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 FD006099/FD/FDA HHS/United States
- R61 HL147833/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN275201000003I/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R33 HL147833/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R13 HD102136/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201300017C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201300017I/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U24 MD016258/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AR069522/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM086330/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN272201500006C/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U18 FD006298/FD/FDA HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical