Integrated analysis of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression reveals increased levels in high-grade glioma
- PMID: 33963441
- PMCID: PMC8236471
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-021-03656-w
Integrated analysis of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression reveals increased levels in high-grade glioma
Abstract
Purpose: Gliomas are the most frequent primary brain tumors of adults. Despite intensive research, there are still no targeted therapies available. Here, we performed an integrated analysis of glioma and programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) in 90 samples including 58 glioma and 32 control brain tissues.
Methods: To identify PD-L1 expression in glioma, we performed immunohistochemical analysis of PD-L1 tumor proportion score (TPS) using the clinically valid PD-L1 22C3 antibody on 90 samples including controls and WHO grade I-IV gliomas.
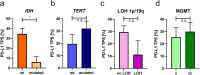
Results: We found that PD-L1 is highly expressed in a subfraction of glioma cells. Analysis of PD-L1 levels in different glioma subtypes revealed a strong intertumoral variation of PD-L1 protein. Furthermore, we correlated PD-L1 expression with molecular glioma hallmarks such as MGMT-promoter methylation, IDH1/2 mutations, TERT promoter mutations and LOH1p/19q.
Conclusion: In summary, we found that PD-L1 is highly expressed in a subfraction of glioma, indicating PD-L1 as a potential new marker in glioma assessment opening up novel therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: Glioblastoma; Glioma; Molecularly targeted therapy; PD-L1; Programmed cell death ligand 1.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Campesato LF, Barroso-Sousa R, Jimenez L, Correa BR, Sabbaga J, Hoff PM, Reis LF, Galante PA, Camargo AA (2015) Comprehensive cancer-gene panels can be used to estimate mutational load and predict clinical benefit to PD-1 blockade in clinical practice. Oncotarget 6(33):34221–34227. 10.18632/oncotarget.5950 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fujita Y, Yagishita S, Hagiwara K, Yoshioka Y, Kosaka N, Takeshita F, Fujiwara T, Tsuta K, Nokihara H, Tamura T, Asamura H, Kawaishi M, Kuwano K, Ochiya T (2015) The clinical relevance of the miR-197/CKS1B/STAT3-mediated PD-L1 network in chemoresistant non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol Ther 23(4):717–727. 10.1038/mt.2015.10 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gatalica Z, Snyder C, Maney T, Ghazalpour A, Holterman DA, Xiao N, Overberg P, Rose I, Basu GD, Vranic S, Lynch HT, Von Hoff DD, Hamid O (2014) Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) in common cancers and their correlation with molecular cancer type. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 23(12):2965–2970. 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-14-0654 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

