Nanoparticle-based approaches to target the lymphatic system for antitumor treatment
- PMID: 33963442
- PMCID: PMC11072902
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-021-03842-6
Nanoparticle-based approaches to target the lymphatic system for antitumor treatment
Abstract
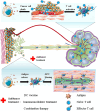
Immunotherapies have been established as safe and efficient modalities for numerous tumor treatments. The lymphatic system, which is an important system, can modulate the immune system via a complex network, which includes lymph nodes, vessels, and lymphocytes. With the deepening understanding of tumor immunology, a plethora of immunotherapies, which include vaccines, photothermal therapy, and photodynamic therapy, have been established for antitumor treatments. However, the deleterious off-target effects and nonspecific targeting of therapeutic agents result in low efficacy of immunotherapy. Fortunately, nanoparticle-based approaches for targeting the lymphatic system afford a unique opportunity to manufacture drugs that can simultaneously tackle both aspects, thereby improving tumor treatments. Over the past decades, great strides have been made in the development of DC vaccines and nanomedicine as antitumor treatments in the field of lymphatic therapeutics and diagnosis. In this review, we summarize the current strategies through which nanoparticle technology has been designed to target the lymphatic system and describe applications of lymphatic imaging for the diagnosis and image-guided surgery of tumor metastasis. Moreover, improvements in the tumor specificity of nanovaccines and medicines, which have been realized through targeting or stimulating the lymphatic system, can provide amplified antitumor immune responses and reduce side effects, thereby promoting the paradigm of antitumor treatment into the clinic to benefit patients.
Keywords: Combinational immunotherapy; DC vaccine; Image-guided therapy; Lymphatic targeting; Lymphoscintigraphy; Nanoplatform; Tumor metastasis.
Figures

References
-
- Ribas A. Adaptive immune resistance: how cancer protects from immune attack. Cancer Discov. 2015;5(9):915. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0563. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

