[Xinfeng capsule inhibits immune inflammation in osteoarthritis by inhibiting the miR- 23a-3p/PETN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway]
- PMID: 33963706
- PMCID: PMC8110458
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.04.02
[Xinfeng capsule inhibits immune inflammation in osteoarthritis by inhibiting the miR- 23a-3p/PETN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway]
Abstract
Objective: To observe the inhibitory effect of Xinfeng capsule (XFC) on immune inflammatory response in the coculture system of chondrocytes and CD4+ T cells from patients with osteoarthritis (OA).
Objective: Thirty OA patients and 30 healthy subjects were examined for the expression of miR-23a-3p/PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR. The changes in the miR-23a-3p/ PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and the clinical indicators of the OA patients after XFC treatment were observed. OA-CD4+ T cells and OA-Chondrocytes cells were cultured in Transwel chambers, and the expressions of miR-23a-3p, PTEN, PI3K, AKT and mTOR mRNA were detected by RT-PCR; the levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α were detected by ELISA. The protein expressions of PTEN, PI3K, AKT, p-AKT, mTOR and p-mTOR were detected by Western blotting.
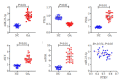
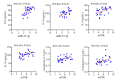
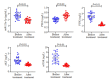
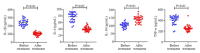
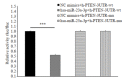
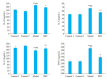
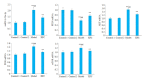
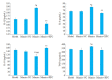
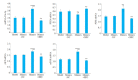
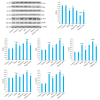
Objective: Compared with healthy individuals, OA patients showed significantly increased expressions of miR-23a-3p, PTEN, PI3K, AKT, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α and lowered expressions of PTEN and IL-10 (P < 0.01). Positive correlations were found between miR-23a-3p and IL-6 and between PI3K and IL-10; mTOR was positively correlated with IL-6, IL-10, complement C3 and C4 (P < 0.01 or 0.05). Intervention with XFC obviously down-regulated the expressions of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α and up-regulated the expression of IL-10 (P < 0.01). In the cell co-culture systems, the expressions of miR-23a-3p, PI3K, Akt, mTOR, IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α were up-regulated while the expressions of PTEN and IL-10 were down-regulated in the model group (P < 0.01). Overexpression of miR-23a-3p significantly up-regulated the expressions of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, miR-23a-3p, PI3K, AKT and mTOR and lowered the expressions of PTEN and IL-10 (P < 0.01 or 0.05). The expressions of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, miR-23a-3p, PI3K, AKT and mTOR were down-regulated and the expressions of IL-10 and PTEN were up-regulated in XFC-treated cells (P < 0.01 or 0.05).
Objective: XFC can reduce the inflammatory response in patients with OA by down-regulating the expression of miR-23a-3p, inhibiting the activation of the PTEN/PI3K/AKT/ mTOR pathway, and regulating the expression of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10 and TNF-α.
目的: 观察新风胶囊(XFC)含药血清通过调控miR-23a-3p /PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路抑制骨关节炎(OA)CD4+T与软骨细胞共培养中免疫炎症反应的作用机制。
方法: 选取30例OA患者(OA组)及30例正常人(NC组)检测miR-23a-3p、10号染色体同源丢失性磷酸酶-张力蛋白基因(PTEN)、磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶(PI3K)、蛋白激酶B(AKT)、哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mTOR)的表达,观察临床指标:红细胞沉降率(ESR)、超敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)、IgA、IgG、IgM、补体C3、补体C4的表达,并观察通路与临床指标的相关性。观察30例OA患者经XFC治疗后通路及临床指标的变化。分离及提取OA-CD4+T细胞,transwell小室培养OA-CD4+T细胞与OA-CH,SD大鼠给药灌胃制备XFC含药血清;采用CCK8法检测OA-软骨细胞的细胞增殖;双荧光素酶报告实验分析miR-23a-3p和PTEN的靶向关系;RT-PCR技术检测共培养细胞中miR-23a-3p、PTENmRNA、PI3KmRNA、AKTmRNA、mTORmRNA的表达;采用ELISA法检测IL-1β、IL-6、IL-10、TNF-α的水平;Western blotting检测PTEN、PI3K、AKT、p-AKT、mTOR、p-mTOR蛋白表达。
结果: 与NC组相比,OA组miR-23a-3p、PTEN、PI3K、AKT、IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α表达显著上调,而PTEN、IL-10表达显著下调(P < 0.01);相关性分析表明:miR-23a-3p与IL-6呈正相关(P < 0.01),PI3K与IL-10呈正相关,mTOR与IL-6、IL-10、补体C3、补体C4呈正相关(P < 0.01或P < 0.05);加入XFC含药血清,miR-23a-3p及PI3K/ AKT/mTOR通路被抑制,L-1β、IL-6、TNF-α表达水平下降、IL-10表达水平升高(P < 0.01);Model组miR-23a-3p、PI3K、AKT、mTOR、IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α表达水平升高,PTEN、IL-10表达水平降低(P < 0.01);miR-23a-3p经过表达后,miR-23a-3p、PI3K、AKT、mTOR、IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α表达水平显著升高,PTEN、IL-10表达水平显著降低(P < 0.01或P < 0.05);XFC组IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α表达降低,IL-10表达升高,miR-23a-3p、PI3K、AKT、mTOR表达下调,PTEN表达上调(P < 0.01或P < 0.05)。
结论: XFC可通过下调miR-23a-3p的表达,抑制PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR通路的活化,改善IL-1β、IL-6,IL-10和TNF-α的表达,降低OA患者炎症反应。
Keywords: PTEN/PI3K/AKT/mTOR; Xinfeng capsule; immuno-inflammatory responses; miR-23a-3p; osteoarthritis.
Figures

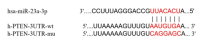
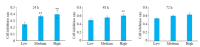
Similar articles
-
[Xinfeng Capsule alleviates RA-FLS-induced angiogenesis in HUVEC cells by inhibiting the lncRNA HOTAIR/PI3K/AKT pathway].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Dec;40(12):1057-1066. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39750043 Chinese.
-
miR-19b-3p relieves intervertebral disc degeneration through modulating PTEN/PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Sep 23;13(18):22459-22473. doi: 10.18632/aging.203553. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34554926 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of Xinfeng Capsule on Beclin1/PI3K-AKT-mTOR of Adjuvant Arthritis Rats].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2017 Apr;37(4):464-469. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 30650507 Chinese.
-
[Xinfeng Capsule alleviates interleukin-1β-induced chondrocyte inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation by regulating the miR-502-5p/TRAF2/NF-κB axis].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Jan 20;44(1):108-118. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.01.13. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 38293982 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway promotes autophagy of articular chondrocytes and attenuates inflammatory response in rats with osteoarthritis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 May;89:1252-1261. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.130. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28320092
Cited by
-
Congenital microtia patients: the genetically engineered exosomes released from porous gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel for downstream small RNA profiling, functional modulation of microtia chondrocytes and tissue-engineered ear cartilage regeneration.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Mar 28;20(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01352-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35346221 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of Benzophenone-3 on osteoarthritis pathogenesis: a network toxicology approach.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Dec 3;13(6):tfae199. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae199. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39677492
-
MiR-29a-3p mediates phosphatase and tensin homolog and inhibits osteoarthritis progression.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Mar 12;24(2):54. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01327-w. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38467932
-
Network Pharmacology-Based Prediction and Verification of the Potential Targets of Pinoresinol Diglucoside for OA Treatment.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Apr 16;2022:9733742. doi: 10.1155/2022/9733742. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35469160 Free PMC article.
-
Complement 3 and 4 impact in osteoarthritis.Biomark Med. 2025 Feb;19(3):81-90. doi: 10.1080/17520363.2024.2409062. Epub 2025 Feb 2. Biomark Med. 2025. PMID: 39893562
References
-
- Xia BJ, DiChen, Zhang JS, et al. Osteoarthritis pathogenesis: a review of molecular mechanisms. Calcif Tissue Int. 2014;95(6):495–505. doi: 10.1007/s00223-014-9917-9. [Xia BJ, DiChen, Zhang JS, et al. Osteoarthritis pathogenesis: a review of molecular mechanisms[J]. Calcif Tissue Int, 2014, 95(6): 495-505.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- GBD disease and injury incidence and prevalence collaborators global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015. Lancet. 2016;388(10053):1545–602. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6. [GBD disease and injury incidence and prevalence collaborators. global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2015[J]. Lancet, 2016, 388(10053): 1545-602.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bijlsma JW, Berenbaum F, Lafeber FP. Osteoarthritis: an update with relevance for clinical practice. Lancet. 2011;377(9783):2115–26. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60243-2. [Bijlsma JW, Berenbaum F, Lafeber FP. Osteoarthritis: an update with relevance for clinical practice[J]. Lancet, 2011, 377(9783): 2115-26.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu Q, Zhang X, Dai L, et al. Long noncoding RNA related to cartilage injury promotes chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(4):969–78. doi: 10.1002/art.38309. [Liu Q, Zhang X, Dai L, et al. Long noncoding RNA related to cartilage injury promotes chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2014, 66(4): 969-78.] - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
