Frequency of cardiac arrhythmias in older adults: Findings from the Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation and Risk of Ischemic Stroke (SAFARIS) study
- PMID: 33965468
- PMCID: PMC8243841
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2021.05.006
Frequency of cardiac arrhythmias in older adults: Findings from the Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation and Risk of Ischemic Stroke (SAFARIS) study
Abstract
Background: Prolonged monitoring of cardiac rhythm has been used to screen for subclinical atrial fibrillation (AF); little is known about other arrhythmias in the general population, especially in the elderly, who are at higher risk of arrhythmias.
Methods: We evaluated the frequency of arrhythmias in the tri-ethnic (white, Black, Hispanic), community-based Subclinical Atrial Fibrillation and Risk of Ischemic Stroke (SAFARIS) study using a patch-based recorder for up to 14 days in 527 participants free of AF, congestive heart failure (CHF) or history of stroke. Differences according to gender, age, ethnicity and presence of hypertension, diabetes and pertinent ECG and echocardiographic variables were examined.
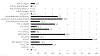
Results: Mean age was 77.2 ± 6.8 years (37.2% men, 62.8% women). AF was present in 10 participants (1.9%), only 2 of them symptomatic. Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and ventricular tachycardia (VT) episodes were observed in 84.4% and 25.0% but only 13.5% and 10.6% of participants reported symptoms, respectively. Severe bradycardia (<40 bpm) was present in 12.5%. Sinus pauses and high-degree atrioventricular blocks were infrequent (2.1% and 1.5%, respectively). Most arrhythmias were more frequent in participants > 75 years; ventricular arrhythmias and severe bradycardia were more common in men. Whites had significantly more episodes of AF than Hispanics, SVT than Blacks and VT ≥ 10 beats than Hispanics and Blacks. Hypertensives had more episodes of severe bradycardia. LV hypertrophy or LVEF <55% were associated with more frequent ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias.
Conclusions: Prolonged cardiac rhythm monitoring revealed moderate frequency of AF, but higher than expected frequencies of AF-predisposing arrhythmias. Ventricular arrhythmias were relatively frequent, whereas severe bradyarrhythmias were infrequent.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Bradycardia; Cardiac arrhythmias; Cardiac complexes; Electrocardiography; Premature; Tachycardia.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest Dr. Biviano has served an advisory Boards for Boston Scientific and Biosense Webster. Dr. Elkind reports receiving study drug in kind from the BMS-Pfizer Alliance for Eliquis and ancillary funding from Roche for the NIH-funded ARCADIA trial of apixaban vs aspirin for stroke prevention; and Dr. Elkind's institution, Columbia University, received payments through a service agreement for his participation in analyses of study data. Dr. Elkind received no personal compensation for any of these activities. Dr. Homma reports being a consultant for St. Jude Medical, Daiichi-Sankyo, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Pfizer. Dr. Sacco has received research grants from NINDS, NCATS, AHA, Evelyn McKnight Brain Foundation and Boehringer Ingelheim. The other authors have no disclosures.
Figures
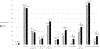


References
-
- Stahrenberg R, Weber-Kruger M, Seegers J, Edelmann F, Lahno R, Haase B, et al. Enhanced detection of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation by early and prolonged continuous holter monitoring in patients with cerebral ischemia presenting in sinus rhythm. Stroke. 2010;41(12):2884–8. - PubMed
-
- Gladstone DJ, Spring M, Dorian P, Panzov V, Thorpe KE, Hall J, et al. Atrial fibrillation in patients with cryptogenic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(26):2467–77. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

