The child behavior checklist can aid in characterizing suspected comorbid psychopathology in clinically referred youth with ADHD
- PMID: 33965736
- PMCID: PMC9069333
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.04.028
The child behavior checklist can aid in characterizing suspected comorbid psychopathology in clinically referred youth with ADHD
Abstract
Objective: To examine the utility of the Child Behavior Checklist (CBCL) to aid in the identification of comorbid psychopathological conditions affecting referred youth with suspected ADHD prior to the evaluation. The CBCL is an easy-to-use assessment tool that may provide invaluable information regarding the severity and characteristics of the presenting complaints.
Methods: The sample included 332 youths consecutively referred to an ADHD program for the assessment of suspected ADHD. Parents completed the CBCL, parent-rated ADHD Self-Report Scale (ASRS), Social Responsiveness Scale (SRS), and Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function (BRIEF). Because of the established association between the CBCL Attention Problems scale and a structured diagnostic interview of ADHD, all youths analyzed had abnormal Attention Problems T-scores (≥60).
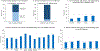
Results: Seventy-six percent of youths with elevated Attention Problems T-scores had ≥3 additional abnormal CBCL scales, suggesting they were likely affected with multiple comorbid psychopathological conditions. Moreover, 44% had ≥1 CBCL clinical scale with a T-score more severe than their Attention Problems T-score, suggesting the putative comorbid condition was more severe than the ADHD symptoms. Additional CBCL scale elevations were associated with more severe functional impairments as assessed by the ASRS, SRS, BRIEF, and CBCL competence scales.
Conclusion: The CBCL obtained before the clinical assessment identified high rates of comorbid psychopathology in youths referred for the assessment of ADHD. It provided detailed information about the types and severity of suspected psychopathological conditions impacting a particular youth, which is critical to guide the assessing clinician on likely differing needs of the affected child.
Keywords: ADHD; Child behavior checklist; Comorbid psychopathology; Pediatric.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosures
Dr. Joseph Biederman is currently receiving research support from the following sources: AACAP, Feinstein Institute for Medical Research, Food & Drug Administration, Genentech, Headspace Inc., NIDA, Pfizer Pharmaceuticals, Roche TCRC Inc., Shire Pharmaceuticals Inc., Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc., Tris, and NIH.
Dr. Carrie Vaudreuil is currently receiving research support from the Louis V. Gerstner III Research Scholar Program.
Dr. Janet Wozniak receives research support from PCORI and Demarest Lloyd, Jr. Foundation. In the past, Dr. Wozniak has received research support, consultation fees or speaker’s fees from Eli Lilly, Janssen, Johnson and Johnson, McNeil, Merck/Schering-Plough, the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Pfizer, and Shire. She is the author of the book
In the past year, Dr. Faraone received income, potential income, travel expenses continuing education support and/or research support from Rhodes, OnDosis, Tris, Otsuka, Arbor, Ironshore, Takeda, Akili, Sunovion, Supernus and Genomind. With his institution, he has US patent US20130217707 A1 for the use of sodium-hydrogen exchange inhibitors in the treatment of ADHD. In previous years, he received support from: Shire, Ironshore, Enzymotec, Neurovance, Alcobra, Rhodes, CogCubed, KemPharm, Enzymotec, Akili, Neurolifesciences, Lundbeck/Takeda, Otsuka, McNeil, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer and Eli Lilly. He also receives royalties from books published by Guilford Press:
Dr. Mai Uchida is partially supported by a K award, grant number 1K23MH122667-01.
Ms. Maura DiSalvo, Ms. K. Yvonne Woodworth, Ms. Abigail Farrell, and Ms. Allison Green do not have any financial relationships to disclose.
Figures
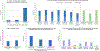
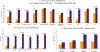
References
-
- Achenbach TM, 1991. Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist/4-18 and the 1991 Profile. University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry, Burlington, VT.
-
- Adler LA, Spencer T, Faraone SV, Kessler RC, Howes MJ, Biederman J, Secnik K, 2006. Validity of pilot adult ADHD self report scale (ASRS) to rate adult ADHD symptoms. Ann Clin Psychiatry 18(3), 145–148. - PubMed
-
- Antshel KM, 2015. Psychosocial interventions in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: update. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am 24(1), 79–97. - PubMed
-
- Biederman J, Ball SW, Monuteaux MC, Kaiser R, Faraone SV, 2008. CBCL clinical scales discriminate ADHD youth with structured-interview derived diagnosis of oppositional defiant disorder (ODD). J Atten Disord 12(1), 76–82. - PubMed
-
- Biederman J, Faraone SV, Doyle AE, Lehman BK, Kraus I, Perrin J, Tsuang MT, 1993a. Convergence of the Child Behavior Checklist with structured interview- based psychiatric diagnoses of ADHD children with and without comorbidity. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry 34(7), 1241–1251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

