Physics-based reconstruction methods for magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 33966457
- PMCID: PMC8107652
- DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2020.0196
Physics-based reconstruction methods for magnetic resonance imaging
Erratum in
-
Correction to 'Physics-based reconstruction methods for magnetic resonance imaging'.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2021 Sep 20;379(2206):20210242. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2021.0242. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2021. PMID: 34334026 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
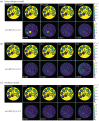
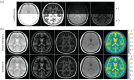
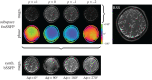
Conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is hampered by long scan times and only qualitative image contrasts that prohibit a direct comparison between different systems. To address these limitations, model-based reconstructions explicitly model the physical laws that govern the MRI signal generation. By formulating image reconstruction as an inverse problem, quantitative maps of the underlying physical parameters can then be extracted directly from efficiently acquired k-space signals without intermediate image reconstruction-addressing both shortcomings of conventional MRI at the same time. This review will discuss basic concepts of model-based reconstructions and report on our experience in developing several model-based methods over the last decade using selected examples that are provided complete with data and code. This article is part of the theme issue 'Synergistic tomographic image reconstruction: part 1'.
Keywords: inverse problems; magnetic resonance imaging; model-based reconstruction.
Figures
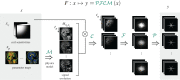
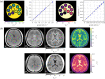

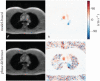
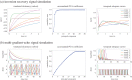
References
-
- Graff C, Li Z, Bilgin A, Altbach MI, Gmitro AF, Clarkson EW. 2006. Iterative T2 estimation from highly undersampled radial fast spin-echo data. ISMRM 14th Scientific Meeting & Exhibition, Seattle 2006. Proc. Int. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 14, 925.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
