Alterations of Kiss 1 receptor, GnRH receptor and nuclear receptors of the hypothalamo-pituitary-ovarian axis following low dose bisphenol-A exposure in Wistar rats
- PMID: 33967032
- PMCID: PMC8225470
- DOI: 10.5115/acb.20.215
Alterations of Kiss 1 receptor, GnRH receptor and nuclear receptors of the hypothalamo-pituitary-ovarian axis following low dose bisphenol-A exposure in Wistar rats
Abstract
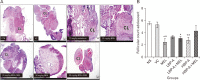
Bisphenol A is a chemical used primarily as a monomer in the production of polycarbonate plastics and epoxy resins. It is a synthetic chemical compound that is produced in billions of pounds annually, and tagged as an endocrine disruptor. Bisphenol A is a high production synthetic chemical compound that is used in the production of many consumables and equipments of daily consumption and use by man. Growing interest in possible health threats posed by endocrine disrupting chemicals (bisphenol-A inclusive), as these substances are in our environment, food, and many consumer products. Therefore, this study aims to determine bisphenol-A effects on the hypothalamo-pituitary-ovarian axis, and role of melatonin in this regard. Forty-two Wistar rats were bred, grouped into 7, with each group consisting of 6 rats. Experimental groups were administered low and high doses of bisphenol-A and melatonin, starting from day 19, and was continued for 7 weeks orally. They were left to develop into full adults and were sacrificed on day 120±4 days. Blood samples, hypothalamus, pituitary and ovarian tissues were excised for biochemical and tissue antioxidants assays as well as genetic studies. Results show elevated gonadotropin and androgen levels. There was disruption of reactive oxygen species in the ovarian tissues, as well as alterations in the expression of genes that regulate reproduction at the hypothalamus and pituitary levels. Conclusion of early exposure to bisphenol-A is associated with prolonged duration of disruption of reproductive functions in female Wistar rats, which persist long after cessation of the exposure. Melatonin antioxidant effects give some promising outturns against bisphenol-A induced toxicities.
Keywords: Bisphenol A; Endocrine disruptors; Hypothalamo-pituitary-ovarian axis; Melatonin; Reproduction.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Impact of low-dose chronic exposure to bisphenol A and its analogue bisphenol B, bisphenol F and bisphenol S on hypothalamo-pituitary-testicular activities in adult rats: A focus on the possible hormonal mode of action.Food Chem Toxicol. 2018 Nov;121:24-36. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.08.024. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 30120946
-
Environmental obesogen tributyltin chloride leads to abnormal hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis function by disruption in kisspeptin/leptin signaling in female rats.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017 Mar 15;319:22-38. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.01.021. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28161095
-
Delayed onset of puberty in male offspring from bisphenol A-treated dams is followed by the modulation of gene expression in the hypothalamic-pituitary-testis axis in adulthood.Reprod Fertil Dev. 2017 Nov;29(12):2496-2505. doi: 10.1071/RD17107. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2017. PMID: 28641706
-
Fighting Bisphenol A-Induced Male Infertility: The Power of Antioxidants.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 15;10(2):289. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020289. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of endocrine-disrupting chemical exposure in the mammalian hypothalamic-pituitary axis.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020 Dec 1;518:110997. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.110997. Epub 2020 Aug 22. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32841708 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of melatonin on the Bisphenol-A- induced cytotoxicity and genetic toxicity in colon cancer cell lines, normal gingival cell lines, and bone marrow stem cell lines.Cancer Inform. 2021 Nov 17;20:11769351211056295. doi: 10.1177/11769351211056295. eCollection 2021. Cancer Inform. 2021. PMID: 34819716 Free PMC article.
-
Endocrine disruptor chemicals, adipokines and reproductive functions.Endocrine. 2022 Nov;78(2):205-218. doi: 10.1007/s12020-022-03061-4. Epub 2022 Apr 27. Endocrine. 2022. PMID: 35476178 Review.
-
Different types of bisphenols alter ovarian steroidogenesis: Special attention to BPA.Heliyon. 2023 Jun 1;9(6):e16848. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16848. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37303564 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kamel AH, Foaud MA, Moussa HM. The adverse effects of bisphenol A on male albino rats. J Basic Appl Zool. 2018;79:6. doi: 10.1186/s41936-018-0015-9. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
