HIF - 1 α may promote glycolysis in psoriasis vulgaris via upregulation of CD147 and GLUT1
- PMID: 33967078
- PMCID: PMC10930304
- DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2021.200010
HIF - 1 α may promote glycolysis in psoriasis vulgaris via upregulation of CD147 and GLUT1
Abstract
Objectives: To analyze the expressions and distributions of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α), CD147, and glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) in epidermis from psoriasis vulgaris and normal people, and to explore the associations among these proteins and their roles in hypoxic HaCaT cell line.
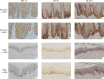
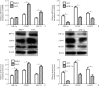
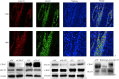
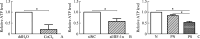
Methods: The expression levels of HIF-1α, CD147, and GLUT1 were determined by immunohistochemistry staining in skin biopsies from 48 psoriasis vularis patients and 33 healthy subjects. Cobalt chloride (CoCl2) was added into the culture media of HaCaT cells to mimic hypoxia while RNA interference and transfection technologies were used to explore the association among these proteins by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting. Glycolytic capacity was detected by ATP and lactate measurements.
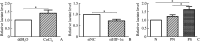
Results: HIF-1α, CD147, and GLUT1 were highly expressed and the glycolytic capacity was increased in lesions of psoriasis vulgaris; HIF-1α upregulated the expression of CD147 and GLUT1, increased the lactate production and decreased the ATP level in CoCl2-treated HaCaT cells, while CD147 and GLUT1 directly or indirectly bound to each other.
Conclusions: Glycolytic capacity increases in the injured keratinocytes of psoriasis vulgaris, suggesting that HIF-1α, CD147, and GLUT1 are associated with glycolysis, which can be considered as the promising targets for psoriasis therapy.
目的: 分析缺氧诱导因子1α(hypoxia-inducible factor-1α,HIF-1α)、白细胞分化抗原147(CD147)及葡萄糖转运蛋白1(glucose transporter 1,GLUT1)在寻常型银屑病皮损和正常人表皮中的分布与表达,并探索这些蛋白质之间的关联及其在缺氧的人永生化表皮细胞(HaCaT细胞)中的作用。方法: 采用免疫组织化学法分析48例寻常型银屑病患者及33例正常人皮肤活检组织中HIF-1α、CD147和GLUT1蛋白质的表达;在HaCaT细胞系中运用氯化钴诱导缺氧、RNA干扰和转染技术后,通过实时RT-PCR和蛋白质印迹法探索蛋白质间的关联;通过检测ATP和乳酸浓度反映皮肤组织和HaCaT细胞的糖酵解能力。结果: 寻常型银屑病皮损中HIF-1α,CD147,GLUT1的表达增加及糖酵解能力增强;在诱导HaCaT细胞缺氧的过程中,HIF-1α使CD147和GLUT1的表达增加,同时乳酸浓度升高及ATP浓度降低,而CD147和GLUT1之间也存在直接或间接的结合。结论: 糖酵解能力在寻常型银屑病皮损中增强,提示与其有关的HIF-1α,CD147,GLUT1可作为银屑病潜在的治疗靶点。.
目的: 分析缺氧诱导因子1α(hypoxia-inducible factor-1α,HIF-1α)、白细胞分化抗原147(CD147)及葡萄糖转运蛋白1(glucose transporter 1,GLUT1)在寻常型银屑病皮损和正常人表皮中的分布与表达,并探索这些蛋白质之间的关联及其在缺氧的人永生化表皮细胞(HaCaT细胞)中的作用。
方法: 采用免疫组织化学法分析48例寻常型银屑病患者及33例正常人皮肤活检组织中HIF-1α、CD147和GLUT1蛋白质的表达;在HaCaT细胞系中运用氯化钴诱导缺氧、RNA干扰和转染技术后,通过实时RT-PCR和蛋白质印迹法探索蛋白质间的关联;通过检测ATP和乳酸浓度反映皮肤组织和HaCaT细胞的糖酵解能力。
结果: 寻常型银屑病皮损中HIF-1α,CD147,GLUT1的表达增加及糖酵解能力增强;在诱导HaCaT细胞缺氧的过程中,HIF-1α使CD147和GLUT1的表达增加,同时乳酸浓度升高及ATP浓度降低,而CD147和GLUT1之间也存在直接或间接的结合。
结论: 糖酵解能力在寻常型银屑病皮损中增强,提示与其有关的HIF-1α,CD147,GLUT1可作为银屑病潜在的治疗靶点。
Keywords: CD147; glucose transporter 1; glycolysis; hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; psoriasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How does hypoxia inducible factor-1α participate in enhancing the glycolysis activity in cervical cancer?Ann Diagn Pathol. 2013 Jun;17(3):305-11. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2012.12.002. Epub 2013 Feb 1. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23375385 Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1alpha promotes hypoxia-induced A549 apoptosis via a mechanism that involves the glycolysis pathway.BMC Cancer. 2006 Jan 27;6:26. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-6-26. BMC Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16438736 Free PMC article.
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor regulates glucose metabolism through glucose transporter 1 induced by hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in adipocytes.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011 Nov;43(11):1602-11. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.07.009. Epub 2011 Jul 26. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011. PMID: 21810481
-
Induction of glucose transporter 1 expression through hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha under hypoxic conditions in trophoblast-derived cells.J Endocrinol. 2004 Oct;183(1):145-54. doi: 10.1677/joe.1.05599. J Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15525582
-
HIF-1alpha modulates energy metabolism in cancer cells by inducing over-expression of specific glycolytic isoforms.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2009 Aug;9(9):1084-101. doi: 10.2174/138955709788922610. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19689405 Review.
Cited by
-
Research Progress on Glycolysis Mechanism of Psoriasis.Psoriasis (Auckl). 2024 Dec 31;14:195-206. doi: 10.2147/PTT.S493315. eCollection 2024. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2024. PMID: 39759475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1 in Bladder Cancer.Curr Mol Med. 2024;24(7):827-834. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666230720163448. Curr Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 37475553 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breaking the psoriasis pathological signaling cycle: A novel nanomedicine strategy targeting metabolism and oxidative stress.Mater Today Bio. 2025 May 23;32:101887. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101887. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40520564 Free PMC article.
-
Keratin 17 covalently binds to alpha-enolase and exacerbates proliferation of keratinocytes in psoriasis.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jul 3;19(11):3395-3411. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.83141. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37497003 Free PMC article.
-
Crucial Role of RLIP76 in Promoting Glycolysis and Tumorigenesis by Stabilization of HIF-1α in Glioma Cells Under Hypoxia.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Nov;59(11):6724-6739. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02999-w. Epub 2022 Aug 23. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35998001
References
-
- Haider AS, Peters SB, Kaporis H, et al. . Genomic analysis defines a cancer-specific gene expression signature for human squamous cell carcinoma and distinguishes malignant hyperproliferation from benign hyperplasia[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2006, 126(4): 869-881. - PubMed
-
- Boffetta P, Gridley G, Lindelöf B. Cancer risk in a population-based cohort of patients hospitalized for psoriasis in Sweden[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2001, 117(6): 1531-1537. - PubMed
-
- Chen C, Pore N, Behrooz A, et al. . Regulation of glut1 mRNA by hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Interaction between H-ras and hypoxia[J]. J Biol Chem, 2001, 276(12): 9519-9525. - PubMed
-
- Fan JY, Yang Y, Xie JY, et al. . MicroRNA-144 mediates metabolic shift in ovarian cancer cells by directly targeting Glut1[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(5): 6855-6860. - PubMed
-
- Fan R, Hou WJ, Zhao YJ, et al. . Overexpression of HPV16 E6/E7 mediated HIF-1α upregulation of GLUT1 expression in lung cancer cells[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(4): 4655-4663. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

