Bacterial Flora in the Sphenoid Sinus Changes with Perioperative Prophylactic Antibiotic Administration
- PMID: 33967178
- PMCID: PMC8258010
- DOI: 10.2176/nmc.oa.2020-0387
Bacterial Flora in the Sphenoid Sinus Changes with Perioperative Prophylactic Antibiotic Administration
Abstract
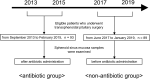
The complications of endonasal transsphenoidal surgery (ETSS) include meningitis and sinusitis, and these complications are troublesome. Some reports have investigated the type of bacteria and the susceptibility of sphenoid sinus mucosal flora to drugs. However, most specimens can be collected after perioperative antibiotic administration. In this study, 95 and 103 sphenoid sinus mucosal samples collected during ETSS from September 2013 to February 2015 and from June 2017 to January 2019, respectively, were examined for bacterial culture. Sphenoid sinus mucosal samples were collected after antibiotic administration in the first period, whereas samples were collected before antibiotic administration in the second period. Hence, the specimens in the second period were not affected by antibiotics. Moreover, drug susceptibility tests for the detected bacteria were performed. Overall, 52 and 51 bacterial isolates were collected during both periods. Gram-positive cocci (GPCs), including Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis, were more common in the non-antibiotic group than in the antibiotic group (p <0.01). However, the proportion of gram-negative rods (GNRs) did not significantly differ between the two groups (p = 0.54). The antibiotic group had a significantly higher proportion of bacteria resistant to ampicillin (p <0.01) and first-generation cephalosporin (p = 0.01) than the non-antibiotic group. In conclusion, there was a difference in bacterial flora in the sphenoid sinus mucosal samples collected before and after intraoperative antibiotic administration.
Keywords: bacterial flora; sphenoid sinus; transsphenoidal surgery.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of the bacterial flora in the nasal cavity and the sphenoid sinus mucosa in patients operated on with an endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014;54(12):1009-13. doi: 10.2176/nmc.oa.2014-0129. Epub 2014 Nov 29. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014. PMID: 25446386 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the bacterial flora in the nasal cavity and the sphenoid sinus mucosa in patients operated on with an endoscopic endonasal transsphenoidal approach.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014;54 Suppl 3:1009-13. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2014. PMID: 26236811
-
Ultra-short antibiotic prophylaxis guided by preoperative microbiological nasal swabs in endoscopic endonasal skull base surgery.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2021 Feb;163(2):369-382. doi: 10.1007/s00701-020-04560-x. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2021. PMID: 32901395
-
A review of eight cases of cavernous sinus thrombosis secondary to sphenoid sinusitis, including a12-year-old girl at the present department.Infect Dis (Lond). 2017 Sep;49(9):641-646. doi: 10.1080/23744235.2017.1331465. Epub 2017 May 23. Infect Dis (Lond). 2017. PMID: 28535728 Review.
-
Gram-negative meningitis associated with transsphenoidal surgery: case reports and review.Clin Infect Dis. 1994 Apr;18(4):553-6. doi: 10.1093/clinids/18.4.553. Clin Infect Dis. 1994. PMID: 8038309
Cited by
-
A study on the effectiveness of multiple intraoperative disinfections and bacteriological monitoring in reducing postoperative intracranial infection rates in transnasal endoscopic skull base surgery.Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2025 Mar 26;167(1):91. doi: 10.1007/s00701-025-06498-4. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2025. PMID: 40138048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hattori Y, Tahara S, Aso S, et al. : Pituitary surgery's epidemiology using a national inpatient database in Japan. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 162: 1317–1323, 2020 - PubMed
-
- Milanese L, Zoli M, Sollini G, et al. : Antibiotic prophylaxis in endoscopic endonasal pituitary and skull base surgery. World Neurosurg 106: 912–918, 2017 - PubMed
-
- Ivan ME, Iorgulescu JB, El-Sayed I, et al. : Risk factors for postoperative cerebrospinal fluid leak and meningitis after expanded endoscopic endonasal surgery. J Clin Neurosci 22: 48–54, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Borg A, Kirkman MA, Choi D: Endoscopic endonasal anterior skull base surgery: a systematic review of complications during the past 65 years. World Neurosurg 95: 383–391, 2016 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical