Bioelectric impedance analysis for body composition measurement and other potential clinical applications in critical illness
- PMID: 33967207
- PMCID: PMC8270506
- DOI: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000840
Bioelectric impedance analysis for body composition measurement and other potential clinical applications in critical illness
Abstract
Purpose of review: Insight into body composition is of great value in the ICU. Bioelectric impedance analysis (BIA) is the most applicable bedside technique. However, bioimpedance has not been validated in the critically ill, and the interpretation of the measurements poses challenges. This review discusses the potential clinical applications of BIA and explores caveats and solutions to its use in the intensive care setting.
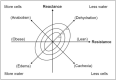
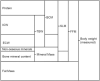
Recent findings: A correlation is repeatedly found between raw impedance parameters, fluid ratios, overhydration, and adverse outcome of critical illness. However, cut-off and reference values remain elusive. Experience with BIA-guided fluid management in the ICU is limited. BIA-derived muscle mass appears a promising biomarker for sarcopenia, correlating well with CT-analysis. Body cell mass and fat-free mass provide potential use in estimation of metabolic rate, protein requirements and pharmacokinetics. Several methods of reducing bias in BIA parameters in critical illness require validation.
Summary: There are currently too many uncertainties and discrepancies regarding interpretation of bioimpedance in critical illness, to justify therapeutic consequences. However, there are several promising areas of research, concerning some of the most urgent clinical problems in intensive care, emphasizing the need to evaluate further the use and interpretation of bioimpedance in the intensive care setting.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kyle UG, Bosaeus I, De Lorenzo AD, et al. . Bioelectrical impedance analysis--part I: review of principles and methods. Clin Nutr 2004; 23:1226–1243. - PubMed
-
- Martinoli R, Mohamed EI, Maiolo C, et al. . Total body water estimation using bioelectrical impedance: a meta-analysis of the data available in the literature. Acta Diabetol 2003; 40: Suppl 1: S203–S206. - PubMed
-
- Mundi MS, Patel JJ, Martindale R. Body composition technology: implications for the ICU. Nutr Clin Pract 2019; 34:48–58. - PubMed
-
A review of clinical relevance, discussing the most commonly available clinical technology for assessment of body composition, including data from trials in critically ill patients highlighting the benefits and weaknesses of each modality.
-
- Barbosa-Silva MC, Barros AJ, Wang J, et al. . Bioelectrical impedance analysis: population reference values for phase angle by age and sex. Am J Clin Nutr 2005; 82:49–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

