Assessing the Burden of Infant Deaths Due to Herpes Simplex Virus, Human Immunodeficiency Virus, and Congenital Syphilis: United States, 1995 to 2017
- PMID: 33967231
- PMCID: PMC8284346
- DOI: 10.1097/OLQ.0000000000001458
Assessing the Burden of Infant Deaths Due to Herpes Simplex Virus, Human Immunodeficiency Virus, and Congenital Syphilis: United States, 1995 to 2017
Abstract
Background: Despite advances in diagnosis and treatment, neonatal infection with herpes simplex virus (HSV) has a high case fatality rate. The national burden of neonatal HSV and associated deaths is unknown because this condition is not nationally notifiable. We investigated trends in HSV-related infant deaths compared with infant deaths from congenital syphilis (CS) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Methods: Linked birth-death files for infant deaths from 1995 to 2017 were obtained from the National Center for Health Statistics. These files include infants who were born alive and died in the first 365 days of life and exclude stillbirths. We searched death certificates for disease codes indicating HSV, CS, or HIV, and calculated the frequency and rate of deaths for each infection, overall, by infant sex, and birthing parent age and race/ethnicity.
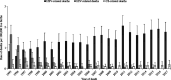
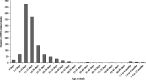
Results: Nationally, 1591 deaths related to the infections of interest were identified: 1271 related to HSV (79.9%), 234 to HIV (14.7%), and 86 to CS (5.4%). Herpes simplex virus-related deaths increased significantly from 0.83/100,000 live births (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.57-1.17) in 1995 to 1.77 (95% CI, 1.37-2.24) in 2017. In contrast, HIV-related deaths declined: 1.64/100,000 (95% CI, 1.27-2.10) in 1995 to 0.00 in 2017. There was a median of 3 CS-related deaths/year, with elevated frequencies in 1995 to 1996 and 2017 (n = 8). Herpes simplex virus-related death rates were elevated among infants born to birthing parents younger than 20 years (4.17/100,000; 95% CI, 3.75-4.59) and to Black parents (2.86/100,000; 95% CI, 2.58-3.15).
Conclusions: Nationally, HSV-related infant deaths exceeded those caused by HIV and CS and seem to be increasing. Our findings underscore the need for an effective HSV vaccine, test technologies enabling rapid identification of infants exposed to HSV at delivery, and a focus on equity in prevention efforts.
Copyright © 2021 Written work prepared by employees of the Federal Government as part of their official duties is, under the U.S. Copyright Act, a “work of the United States Government” for which copyright protection under Title 17 of the United States Code is not available. As such, copyright does not extend to the contributions of employees of the Federal Government.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest and Sources of Funding: The authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest, or nonfinancial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this article.
Figures
References
-
- Pinninti SG, Kimberlin DW. Neonatal herpes simplex virus infections. Semin Perinatol 2018; 42:168–175. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) . Neonatal herpes simplex virus infection following Jewish ritual circumcisions that included direct orogenital suction—New York City, 2000–2011. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2012; 61:405–409. - PubMed
-
- Kimberlin DW Lakeman FD Arvin AM, et al. . Application of the polymerase chain reaction to the diagnosis and management of neonatal herpes simplex virus disease. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Collaborative Antiviral Study Group. J Infect Dis 1996; 174:1162–1167. - PubMed
-
- Kimberlin DW Lin CY Jacobs RF, et al. . Safety and efficacy of high-dose intravenous acyclovir in the management of neonatal herpes simplex virus infections. Pediatrics 2001; 108:230–238. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

