Exploration of nutritional, antioxidative, antibacterial and anticancer status of Russula alatoreticula: towards valorization of a traditionally preferred unique myco-food
- PMID: 33967311
- PMCID: PMC8076386
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-020-04723-9
Exploration of nutritional, antioxidative, antibacterial and anticancer status of Russula alatoreticula: towards valorization of a traditionally preferred unique myco-food
Abstract
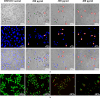
Healthy food trend is becoming popular these days fueling search for ingredients empowered by pharma-nutritional benefits. In contrast, numerous wild-growing mushrooms are traditionally cherished as health promoting gastronomies in India; although credibility of their effects has so far been limited. Hence the present study aimed to unveil a unique tribal cuisine, Russula alatoreticula, with nutritional, chemical and pharmacological relevance. The outcome demonstrated an excellent alimentary composition with carbohydrate and protein as prominent macronutrients in contrast to fat providing oleic acid (36.66%), linoleic acid (16.84%), palmitic acid (16.01%) and stearic acid (15.31%) indicative of profitable nutritive account. Conversely, ethanolic fraction enriched with phenolics (pyrogallol > cinnamic acid) presented effective antioxidant property in terms of radical scavenging, Fe2+ chelating and reducing power with EC50 ranging from 785 to 2500 μg/ml. Remarkable antibacterial activity was also noted against the tested microorganisms (MIC of 72.5-1560 μg/ml) preferentially targeting Gram-positive one. Besides treatment of the preparation rendered Hep3B proliferation as evident by phenotypic changes, cell cycle interference, reactive oxygen species generation, mitochondrial membrane potential reduction, DNA fragmentation, change in Bax/Bcl2 ratio and activation of caspase9 signifying induction of intrinsic mitochondrial pathway. Thus the study represents R. alatoreticula as a value-added bio-resource that could be featured in food and pharmaceutical industries for betterment of humankind.
Keywords: Fatty acid composition; Hep3B human liver cancer; High performance thin layer chromatography (HPLC); Intrinsic mitochondrial pathway; Newly-found ethnic macrofungus.
© Association of Food Scientists & Technologists (India) 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Agrahar-Murugkar D, Subbulakshmi G. Nutritional value of edible wild mushrooms collected from The Khasi Hills of Meghalaya. Food Chem. 2005;89:599–603. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.03.042. - DOI
-
- AOAC (1995) Official methods of analysis, 16th ed. Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Washington DC, USA
-
- Basli A, Belkacem N, Amrani I. Health benefits of phenolic compounds against cancers. In: Soto-Hernández M, Palma-Tenango M, Garcia-Mateos MR, editors. Phenolic compounds. London: IntechOpen; 2017. p. 752.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
