Preoperative physiological esophageal assessment for anti-reflux surgery: A guide for surgeons on high-resolution manometry and pH testing
- PMID: 33967555
- PMCID: PMC8072189
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i16.1751
Preoperative physiological esophageal assessment for anti-reflux surgery: A guide for surgeons on high-resolution manometry and pH testing
Abstract
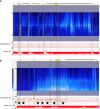
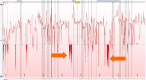
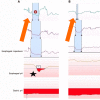
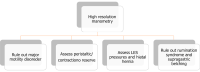
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is one of the most commonly encountered digestive diseases in the world, with the prevalence continuing to increase. Many patients are successfully treated with lifestyle modifications and proton pump inhibitor therapy, but a subset of patients require more aggressive intervention for control of their symptoms. Surgical treatment with fundoplication is a viable option for patients with GERD, as it attempts to improve the integrity of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES). While surgery can be as effective as medical treatment, it can also be associated with side effects such as dysphagia, bloating, and abdominal pain. Therefore, a thorough pre-operative assessment is crucial to select appropriate surgical candidates. Newer technologies are becoming increasingly available to help clinicians identify patients with true LES dysfunction, such as pH-impedance studies and high-resolution manometry (HRM). Pre-operative evaluation should be aimed at confirming the diagnosis of GERD, ruling out any major motility disorders, and selecting appropriate surgical candidates. HRM and pH testing are key tests to consider for patients with GERD like symptoms, and the addition of provocative measures such as straight leg raises and multiple rapid swallows to HRM protocol can assess the presence of underlying hiatal hernias and to test a patient's peristaltic reserve prior to surgery.
Keywords: Anti-reflux surgery; Fundoplication; Gastroesophageal reflux disease; High resolution manometry; Pre-operative assessment; pH-impedance.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors disclose no conflicts of interest or external funding for this publication.
Figures


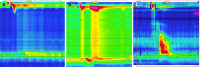

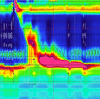


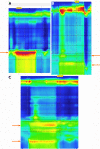
References
-
- Dent J, Becher A, Sung J, Zou D, Agréus L, Bazzoli F. Systematic review: patterns of reflux-induced symptoms and esophageal endoscopic findings in large-scale surveys. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012; 10: 863-873. :e3. - PubMed
-
- Patti MG. An Evidence-Based Approach to the Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. JAMA Surg. 2016;151:73–78. - PubMed
-
- Katz PO, Gerson LB, Vela MF. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:308–28; quiz 329. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

