Potential Networks Regulated by MSCs in Acute-On-Chronic Liver Failure: Exosomal miRNAs and Intracellular Target Genes
- PMID: 33968135
- PMCID: PMC8102832
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.650536
Potential Networks Regulated by MSCs in Acute-On-Chronic Liver Failure: Exosomal miRNAs and Intracellular Target Genes
Abstract
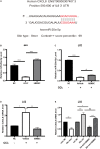
Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) is a severe syndrome associated with high mortality. Alterations in the liver microenvironment are one of the vital causes of immune damage and liver dysfunction. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (hBMSCs) have been reported to alleviate liver injury via exosome-mediated signaling; of note, miRNAs are one of the most important cargoes in exosomes. Importantly, the miRNAs within exosomes in the hepatic microenvironment may mediate the mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-derived regulation of liver function. This study investigated the hepatocyte exosomal miRNAs which are regulated by MSCs and the target genes which have potential in the treatment of liver failure. Briefly, ACLF was induced in mice using carbon tetrachloride and primary hepatocytes were isolated and co-cultured (or not) with MSCs under serum-free conditions. Exosomes were then collected, and the expression of exosomal miRNAs was assessed using next-generation sequencing; a comparison was performed between liver cells from healthy versus ACLF animals. Additionally, to identify the intracellular targets of exosomal miRNAs in humans, we focused on previously published data, i.e., microarray data and mass spectrometry data in liver samples from ACLF patients. The biological functions and signaling pathways associated with differentially expressed genes were predicted using gene ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomics enrichment analyses; hub genes were also screened based on pathway analysis and the prediction of protein-protein interaction networks. Finally, we constructed the hub gene-miRNA network and performed correlation analysis and qPCR validation. Importantly, our data revealed that MSCs could regulate the miRNA content within exosomes in the hepatic microenvironment. MiR-20a-5p was down-regulated in ACLF hepatocytes and their exosomes, while the levels of chemokine C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 8 (CXCL8; interleukin 8) were increased in hepatocytes. Importantly, co-culture with hBMSCs resulted in up-regulated expression of miR-20a-5p in exosomes and hepatocytes, and down-regulated expression of CXCL8 in hepatocytes. Altogether, our data suggest that the exosomal miR-20a-5p/intracellular CXCL8 axis may play an important role in the reduction of liver inflammation in ACLF in the context of MSC-based therapies and highlights CXCL8 as a potential target for alleviating liver injury.
Keywords: acute-on-chronic liver failure; exosome; mesenchymal stem cells; microRNA; multi-omics.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Gao, Lin, Xiong, Wang, Chen, Lin and Gao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stem cell-regulated miRNA-mRNA landscape in acute-on-chronic liver failure.Genomics. 2023 Nov;115(6):110737. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2023.110737. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37926353
-
The analysis of Modified Qing' E Formula on the differential expression of exosomal miRNAs in the femoral head bone tissue of mice with steroid-induced ischemic necrosis of femoral head.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 10;13:954778. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.954778. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36034465 Free PMC article.
-
Lipotoxic hepatocyte-derived exosomal miR-1297 promotes hepatic stellate cell activation through the PTEN signaling pathway in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Apr 14;27(14):1419-1434. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i14.1419. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33911465 Free PMC article.
-
Liver-derived extracellular vesicles from patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure impair hepatic regeneration by inhibiting on FGFR2 signaling via miR-218-5p.Hepatol Int. 2023 Aug;17(4):833-849. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10513-0. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Hepatol Int. 2023. PMID: 37055701 Review.
-
Exosomal microRNAs from mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: Biology and applications in neuroprotection.World J Stem Cells. 2021 Jul 26;13(7):776-794. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v13.i7.776. World J Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 34367477 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The progress to establish optimal animal models for the study of acute-on-chronic liver failure.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 9;10:1087274. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1087274. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36844207 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in pre-conditioned mesenchymal stem/stromal cell (MSCs) therapy in organ failure; a comprehensive review of preclinical studies.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Jun 7;14(1):155. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03374-9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37287066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells exosomal let-7a-5p improve autophagic flux and alleviate liver injury in acute-on-chronic liver failure by promoting nuclear expression of TFEB.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Oct 12;13(10):865. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05303-9. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36224178 Free PMC article.
-
The Immunomodulatory Properties of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Play a Critical Role in Inducing Immune Tolerance after Liver Transplantation.Stem Cells Int. 2021 Sep 4;2021:6930263. doi: 10.1155/2021/6930263. eCollection 2021. Stem Cells Int. 2021. PMID: 34531915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multiomics landscape of serum exosomes during the development of sepsis.J Adv Res. 2022 Jul;39:203-223. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.11.005. Epub 2021 Nov 17. J Adv Res. 2022. PMID: 35777909 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

