PAR2 Promoter Hypomethylation Regulates PAR2 Gene Expression and Promotes Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Progression
- PMID: 33968158
- PMCID: PMC8081642
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/5542485
PAR2 Promoter Hypomethylation Regulates PAR2 Gene Expression and Promotes Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Progression
Abstract
Objective: Protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR2) also known as F2RL1 is a G protein-coupled receptor that intimately correlates with cancer occurrence. DNA methylation turns out a vital mechanism regulating gene expression, while PAR2 promoter methylation is proven to be involved in cancer development. Hence, this study attempted to clarify the molecular mechanism by which PAR2 mediates lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) progression, via identifying the effect of PAR2 promoter methylation on LUAD cell progression.
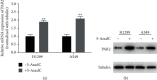
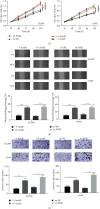
Methods: Associations of PAR2 promoter methylation with PAR2 gene expression and prognosis of LUAD patients were analyzed via bioinformatics analysis. PAR2 promoter methylation and gene expression at the cellular level were measured using methylation-specific PCR, qRT-PCR, and Western blot assays. DNA methyltransferase inhibitor 5-AzadC was used to treat cells to assess PAR2 gene expression alteration. Cell biological behaviors upon PAR2 overexpression were characterized via MTT, wound healing assay, and Transwell assay.
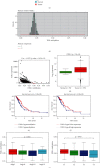
Results: Bioinformatics analysis revealed that PAR2 promoter methylation was negatively related to PAR2 gene expression, while PAR2 promoter hypermethylation and low gene expression indicated favorable LUAD prognosis. Besides, it turned out that PAR2 presented upregulated expression and hypomethylated promoter in LUAD cells. Moreover, PAR2 gene expression was elevated in cells treated with 5-AzadC, and the proliferative, migratory, and invasive capabilities of cells with 5-AzadC or high PAR2 gene expression were all enhanced.
Conclusion: In sum, PAR2 promoter hypomethylation potentiates LUAD cell progression, in turn affecting the prognosis of LUAD patients.
Copyright © 2021 Kuan Wu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
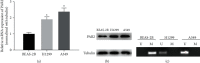
Similar articles
-
PAR2 promotes tumor-associated angiogenesis in lung adenocarcinoma through activating EGFR pathway.Tissue Cell. 2022 Dec;79:101918. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2022.101918. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Tissue Cell. 2022. PMID: 36148733
-
Hypomethylation-associated LINC00987 downregulation induced lung adenocarcinoma progression by inhibiting the phosphorylation-mediated degradation of SND1.Mol Carcinog. 2024 Jul;63(7):1260-1274. doi: 10.1002/mc.23722. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Mol Carcinog. 2024. PMID: 38607240
-
ANLN Regulated by miR-30a-5p Mediates Malignant Progression of Lung Adenocarcinoma.Comput Math Methods Med. 2021 Nov 5;2021:9549287. doi: 10.1155/2021/9549287. eCollection 2021. Comput Math Methods Med. 2021. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Oct 4;2023:9792745. doi: 10.1155/2023/9792745. PMID: 34777569 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Circular RNA cMras inhibits lung adenocarcinoma progression via modulating miR-567/PTPRG regulatory pathway.Cell Prolif. 2019 May;52(3):e12610. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12610. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Cell Prolif. 2019. PMID: 31012177 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of prognostic values of the transcription factor-CpG-gene triplets in lung adenocarcinoma: A narrative review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Dec 16;101(50):e32045. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000032045. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36550923 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNA AC245100.4 contributes to prostate cancer migration via regulating PAR2 and activating p38-MAPK pathway.Med Oncol. 2022 May 16;39(5):94. doi: 10.1007/s12032-022-01689-w. Med Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35570225
-
Comprehensive analysis of a novel signature incorporating lipid metabolism and immune-related genes for assessing prognosis and immune landscape in lung adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 25;13:950001. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.950001. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36091041 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of driver genes with potential prognostic implications in lung adenocarcinoma based on H3K79me2.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Oct 7;20:5535-5546. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.10.004. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36249560 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of an immune-related gene prognostic index for lung adenocarcinoma.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Nov 30;15(11):6205-6227. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1374. Epub 2023 Nov 24. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 38090291 Free PMC article.
-
[Research Progress on Pathogenic Mechanism and Potential Therapeutic Drugs of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Complicated with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022 Oct 20;25(10):756-763. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2022.101.45. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36167462 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Rakash S. Role of proteases in cancer: a review. Biotechnology and Molecular Biology Reviews. 2012;7(4):90–101. doi: 10.5897/bmbr11.027. - DOI
-
- Kim K. Y., Yoon M., Cho Y., et al. Targeting metastatic breast cancer with peptide epitopes derived from autocatalytic loop of Prss14/ST14 membrane serine protease and with monoclonal antibodies. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research. 2019;38(1):p. 363. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1373-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nathalie H.-V.’h., Chris P., Serge G., et al. High kallikrein-related peptidase 6 in non-small cell lung cancer cells: an indicator of tumour proliferation and poor prognosis. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine. 2009;13(9b):4014–4022. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2009.00763.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

