Interleukin-1 induces receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand-independent osteoclast differentiation in RAW264.7 cells
- PMID: 33968171
- PMCID: PMC8097200
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10072
Interleukin-1 induces receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand-independent osteoclast differentiation in RAW264.7 cells
Abstract
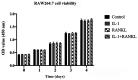
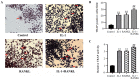
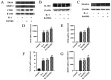
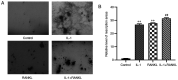
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is a pro-inflammatory cytokine which induces bone destruction in various diseases, such as osteoporosis and rheumatoid arthritis. RAW264.7 cells are frequently used in studies as osteoclast precursors, however it remains unclear whether IL-1 can induce osteoclast differentiation from RAW264.7 cells without the stimulation of receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL). Hence, the present study aimed to investigate the effects of IL-1 on the formation of osteoclasts from RAW264.7 cells. The cell viability was determined via the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay. Protein and gene expression were measured by western blotting and reverse transcription-quantitative PCR, respectively. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining and the resorption pit assay were performed to determine the formation and activity of osteoclasts. A significantly increased quantity of osteoclasts were found in the IL-1 group compared with the control group, and also in the RANKL+IL-1 group compared with the RANKL group. In addition IL-1 significantly increased both the protein and mRNA expression of specific genes associated with osteoclastogenesis, including nuclear factor of activated T cells cytoplasmic 1, matrix metalloprotein-9, cathepsin K and TRAP. The findings of the present study suggested that IL-1 can induce osteoclast differentiation and upregulate the quantity of osteoclasts differentiated from RAW264.7 cells. These results may lay a foundation for further study of diseases involving inflammation-associated bone loss. The combined blockade of IL-1 and RANKL may be effective for the prevention of inflammatory bone loss.
Keywords: RAW264.7 cells; interleukin-1; osteoclast differentiation; osteoporosis; receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand-independent.
Copyright: © Liao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand induces the expression of carbonic anhydrase II, cathepsin K, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in osteoclast precursor RAW264.7 cells.Life Sci. 2007 Mar 13;80(14):1311-8. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2006.12.037. Epub 2007 Jan 23. Life Sci. 2007. PMID: 17306833
-
Conjugated linoleic acid inhibits osteoclast differentiation of RAW264.7 cells by modulating RANKL signaling.J Lipid Res. 2006 Aug;47(8):1739-48. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M600151-JLR200. Epub 2006 May 15. J Lipid Res. 2006. PMID: 16702601
-
Interleukin 26 suppresses receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand induced osteoclastogenesis via down-regulation of nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 and nuclear factor κB activity.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016 Nov;55(11):2074-2083. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew302. Epub 2016 Aug 21. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016. PMID: 27550297
-
IL-17A suppresses the expression of bone resorption-related proteinases and osteoclast differentiation via IL-17RA or IL-17RC receptors in RAW264.7 cells.Biochimie. 2010 Apr;92(4):398-404. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2009.12.011. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Biochimie. 2010. PMID: 20045440
-
Interleukin 29 inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis via activation of JNK and STAT, and inhibition of NF-κB and NFATc1.Cytokine. 2019 Jan;113:144-154. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.06.032. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 30001863
Cited by
-
B cells enhance IL-1 beta driven invasiveness in triple negative breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 16;15(1):2211. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86064-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39820772 Free PMC article.
-
The Ethanol Extracts of Osmanthus fragrans Leaves Ameliorate the Bone Loss via the Inhibition of Osteoclastogenesis in Osteoporosis.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 5;12(2):253. doi: 10.3390/plants12020253. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36678965 Free PMC article.
-
Eucommia, Cuscuta, and Drynaria Extracts Ameliorate Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis by Inhibiting Osteoclastogenesis Through PI3K/Akt Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Feb 4;12:772944. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.772944. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35185535 Free PMC article.
-
B cells enhance IL-1 beta driven invasiveness in triple-negative breast cancer.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 31:rs.3.rs-5153341. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5153341/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 16;15(1):2211. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86064-1. PMID: 39801513 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Roles of Toll-like Receptor Signaling in Inflammatory Bone Resorption.Biology (Basel). 2024 Sep 4;13(9):692. doi: 10.3390/biology13090692. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336119 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
