Protein kinase N1 promotes proliferation and invasion of liver cancer
- PMID: 33968181
- PMCID: PMC8097187
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10083
Protein kinase N1 promotes proliferation and invasion of liver cancer
Abstract
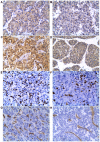
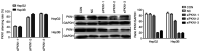
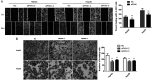
Protein kinase (PK) N1, also called PKC-related protein 1, participates in the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of various malignant tumors. However, the role of PKN1 in liver cancer remains to be elucidated. The present study investigated the expression of PKN1 using immunohistochemistry in surgical specimens from 36 patients and analyzed the correlation with VEGF, microvascular density (MVD), cell proliferation index (Ki67) and clinicopathological parameters. PKN1 was highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and was positively correlated with histological grading of HCC, Ki67 expression and MVD. PKN1 expression in moderately and poorly differentiated HCC was significantly higher compared with highly differentiated HCC. Expression of PKN1 was positively correlated with Ki67 and MVD, and Ki67 expression was positively correlated with MVD. The effects of PKN1 on proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of liver cancer cells were detected in vitro. Cell viability, migration and invasion were reduced and the apoptosis rate was significantly improved when PKN1 expression was silenced in liver cancer cells. Thus, PKN1 serves an important role in the development and progression of liver cancer. Inhibition of PKN1 activity may provide a promising therapeutic target for liver cancer.
Keywords: liver cancer; microvascular density; proliferation; protein kinase N1.
Copyright: © Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of PKN1 in glioma pathogenesis and the antiglioma effect of raloxifene targeting PKN1.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Sep;27(18):2730-2743. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17860. Epub 2023 Jul 21. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37480215 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative analysis of vascular endothelial growth factor, microvascular density and their clinicopathologic features in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2005 May;4(2):220-6. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2005. PMID: 15908319
-
[Relationship between the proliferative activity of cancer cells and microvessel density in portal vein thrombosis and transfer of hepatocellular carcinoma].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2002 Oct;10(5):366-9. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2002. PMID: 12392620 Chinese.
-
PKN1 modulates TGFβ and EGF signaling in HEC-1-A endometrial cancer cell line.Onco Targets Ther. 2014 Aug 4;7:1397-408. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S65051. eCollection 2014. Onco Targets Ther. 2014. PMID: 25120372 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA CRNDE promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through miR-217/MAPK1 axis.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Dec;22(12):5862-5876. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13856. Epub 2018 Sep 24. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30246921 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
VEGF promotes diabetic retinopathy by upregulating the PKC/ET/NF-κB/ICAM-1 signaling pathway.Eur J Histochem. 2022 Oct 27;66(4):3522. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2022.3522. Eur J Histochem. 2022. PMID: 36305269 Free PMC article.
-
The role of PKN1 in glioma pathogenesis and the antiglioma effect of raloxifene targeting PKN1.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Sep;27(18):2730-2743. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17860. Epub 2023 Jul 21. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37480215 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of PKN1 as a Prognosis Biomarker for Endometrial Cancer.Cancer Control. 2022 Jan-Dec;29:10732748221094797. doi: 10.1177/10732748221094797. Cancer Control. 2022. PMID: 35533253 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Flavonoid Derivatives Show Potent Efficacy in Human Lymphoma Models.EJHaem. 2025 Jun 19;6(3):e70081. doi: 10.1002/jha2.70081. eCollection 2025 Jun. EJHaem. 2025. PMID: 40538494 Free PMC article.
-
Target Mapping in Cancer: Ligandable Protein Pockets on 3D OncoPPI Networks.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 25;18(7):958. doi: 10.3390/ph18070958. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732248 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
