Development of GATE Monte Carlo Code for Simulation and Dosimetry of New I-125 Seeds in Eye Plaque Brachytherapy
- PMID: 33968275
- PMCID: PMC8053639
- DOI: 10.1007/s13139-020-00680-5
Development of GATE Monte Carlo Code for Simulation and Dosimetry of New I-125 Seeds in Eye Plaque Brachytherapy
Abstract
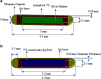
Purpose: Dose distributions are calculated by Monte Carlo (MC) simulations for two low-energy models 125I brachytherapy source-IrSeed-125 and IsoAid Advantage (model IAI-125A)-loaded in the 14-mm standardized plaque of the COMS during treatment of choroid melanoma.
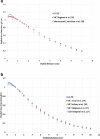
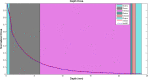
Methods: In this study, at first, the radial dose function in water around 125I brachytherapy sources was calculated based on the recommendations of the Task Group No. 43 American Association of Physicists in Medicine (TG-43U1 APPM) using by GATE code. Then, brachytherapy dose distribution of a new model of the human eye was investigated for a 14-mm COMS eye plaque loaded with these sources with GATE Monte Carlo simulation.
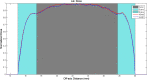
Results: Results show that there are good agreements between simulation results of these sources and reporting measurements and simulations. Dosimetry results in the designed eye phantom for two types of iodine seeds show that the ratios of average dose of tumor to sclera, vitreous, and retina for IrSeed (IsoAid) source are 3.7 (3.7), 6.2 (6.1), and 6.3 (6.3), respectively, which represents the dose saving to healthy tissues. The maximum percentage differences between DVH curve of IsoAid and IrSeed seeds was about 8%.
Conclusions: Our simulation results show that although new model of the 125I brachytherapy source having a slightly larger dimension than IAI-125A, it can be used for eye melanoma treatment because the COMS eye plaque loaded with IrSeed-125 could produce similar results to the IsoAid seeds, which is applicable for clinical plaque brachytherapy for uveal melanoma.
Keywords: Brachytherapy; GATE Monte Carlo; Low-energy sources; Ocular melanoma.
© Korean Society of Nuclear Medicine 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestPayvand Taherparvar and Zeinab Fardi declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Episcleral eye plaque dosimetry comparison for the Eye Physics EP917 using Plaque Simulator and Monte Carlo simulation.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015 Nov 8;16(6):226-239. doi: 10.1120/jacmp.v16i6.5659. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015. PMID: 26699577 Free PMC article.
-
Dosimetry of (125)I and (103)Pd COMS eye plaques for intraocular tumors: report of Task Group 129 by the AAPM and ABS.Med Phys. 2012 Oct;39(10):6161-84. doi: 10.1118/1.4749933. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 23039655
-
A modern Monte Carlo investigation of the TG-43 dosimetry parameters for an 125I seed already having AAPM consensus data.Med Phys. 2014 Feb;41(2):021702. doi: 10.1118/1.4860135. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24506593
-
Monte Carlo dosimetry for 125I and 103Pd eye plaque brachytherapy with various seed models.Med Phys. 2010 Jan;37(1):368-76. doi: 10.1118/1.3271104. Med Phys. 2010. PMID: 20175499
-
Innovations in brachytherapy.Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2025 Feb 25;15(1):62-72. doi: 10.4103/tjo.TJO-D-24-00108. eCollection 2025 Jan-Mar. Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40213297 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
